What is a Content Delivery Network?
A Content Delivery Network is a group of servers placed in different locations that work together to deliver website content quickly. CDNs store cached versions of static files like images, CSS, and JavaScript close to the user’s location. This reduces server load, speeds up page delivery, and improves global website performance.
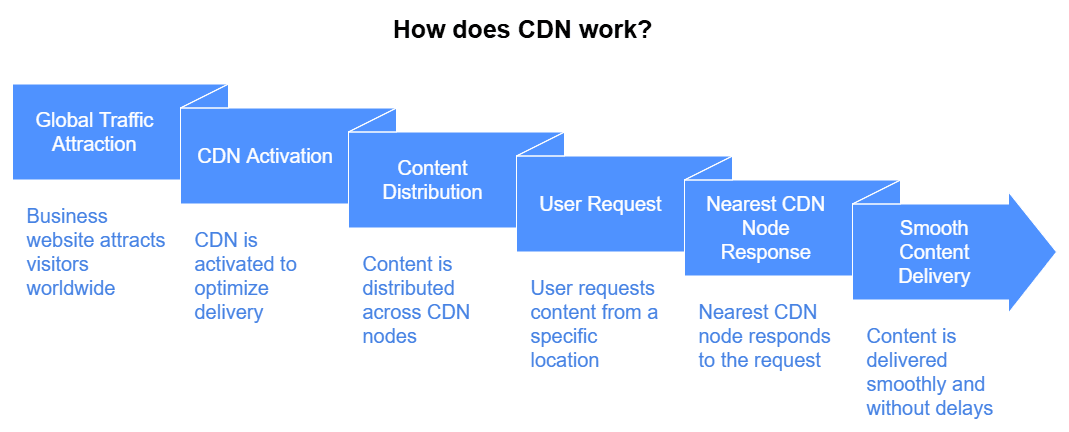
Suppose your business website attracts traffic from all over the globe. In that case, a CDN can ensure that your web pages, images, videos, and other content are delivered smoothly and without delays — no matter where your audience is.
Whether you’re a startup entering the tech ecosystem or an SME looking to expand, CDNs can play a huge role in user retention, page load times, and ultimately, conversion rates.
Why Are CDNs Important?
Content Delivery Networks are no longer a luxury for businesses — they’re a necessity. Here are a few reasons why:
- Improved Speed for Faster Load Times CDNs store cached versions of your website's content in servers across different regions. When someone visits your site, their browser fetches data from the nearest server instead of loading everything from the main server. This results in faster load times. For businesses like those using UI/UX design strategies to enhance user experience, page speed is critical because delays can lose your potential customers.
- Enhanced User Experience Globally Whether users are accessing your site from Tokyo or Toronto, CDNs level the playing field by reducing latency and ensuring consistent performance. If you're a business operating across multiple countries, like Tenet does (operating in over 15 countries!), CDNs are a game-changer. Users expect snappy, lag-free websites — otherwise, they bounce.
- Reduced Server Load Without a CDN, all requests from users funnel into one server, causing it to slow down or even crash if traffic spikes. CDNs distribute this workload, keeping your site scalable even during traffic surges. This is super handy for businesses running PPC campaigns or digital ad promotions that drive sudden bursts of visitors.
- Boost SEO Rankings Google ranks websites partly based on speed and user experience. A fast, reliable website is more likely to rank higher than one that keeps visitors waiting — which means, integrating a CDN can indirectly influence your search engine optimization (SEO) results.
- Increased Security Cyber threats like Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks are unfortunately becoming common. CDNs add an extra layer of security by monitoring and mitigating such attacks, ensuring your data and that of your users is safe.
Key Features of a Content Delivery Network
Not sure what makes a CDN tick? Here are a few notable features to look out for if you’re considering leveraging a CDN for your business website.
- Caching: Stores content on servers closer to end-users so it loads faster.
- Load Balancing: Distributes traffic evenly across servers to avoid overcrowding one server.
- Content Compression: Automatically compresses content for quicker delivery.
- Traffic Analytics: Provides insights into user traffic, enabling smarter decisions for conversion rate optimization (CRO).
- SSL Certificates: Ensures browser-to-server data exchange is encrypted, boosting trust and credibility.
Who Needs a Content Delivery Network?
You should seriously consider a CDN if:
- Your business operates in multiple countries. Whether your user is in LA or London, a CDN ensures your website is lightning-fast no matter the region.
- Your site relies on heavy or dynamic content (videos, images, and pages like e-commerce). These elements can take a while to load without localized servers.
- You want to improve your CRO or user experience design, making your site enjoyable and frustration-free for users.
- You’ve faced scalability issues during traffic spikes. Seasonal promotions or viral campaigns can overload your main server without a CDN.
How Do CDNs Work?
Here’s a simplified breakdown:
- Content Replication: A CDN takes your website’s static content (media files, CSS/JavaScript assets) and replicates it across multiple servers in their network.
- User Request Routing: When a user visits your site, the CDN redirects the request to the server closest to the user’s location.
- File Delivery: The nearest server sends the requested files, resulting in a faster load time.
- Dynamic Optimization: CDNs often utilize algorithms to serve additional personalization or optimize script usage dynamically.
For example, if your business focuses on app development, CDN-optimized apps ensure functionalities work seamlessly during peak user activity.
Common Use Cases of CDNs
CDNs are used almost everywhere on the internet today. Some common applications include:
- Streaming Media: Platforms like Netflix use CDNs to ensure smooth video playback.
- Web Services: Large-scale platforms like Amazon or startups in SaaS development use CDNs to manage their web app delivery.
- E-commerce Platforms: Shopping sites use CDNs to serve product images and text faster, which can directly improve conversion rates.
- Mobile Applications: Having a globally consistent experience is critical for Android and iOS apps. CDNs make sure app load times are consistent worldwide.
How to Choose a CDN Provider for Your Business?
Not all CDNs are created equal. Here’s how to pick the right one for your needs:
- Global Server Availability Make sure the CDN has coverage in regions where most of your audience originates. The better their server reach, the faster the content delivery.
- Performance Metrics Look for performance boosters like low latency and high throughput.
- Security Features Ensure the CDN provides enhanced security, including protection against DDoS attacks and encryption options.
- Scalability If your business often experiences traffic spikes, look for a CDN that can handle scaling.
- Cost-Effectiveness Some CDN services might have additional fees hidden under “bandwidth usage.” Make sure your provider has transparent pricing aligned with your budget.
Ready to Explore CDNs?
If you’re on the journey to building or improving a web or app experience for your business, integrating a strong CDN is a step in the right direction. It’s like having a 24/7 global delivery team getting your content to every corner of the earth without compromise.
