LLM SEO: How to Rank Your Website in AI Search Engines
Share
Share
Get a quick blog summary with
LLMs don’t follow traditional SEO rules, so ranking in their responses takes more than backlinks and keywords.
This guide shows you exactly how to audit your presence, optimize your content, and build the right signals across platforms to earn visibility in AI-generated answers.
If you want your brand to show up when users ask LLMs for recommendations, start here.
⚠️ Disclaimer: There’s no exact blueprint to rank in LLMs yet. But after helping dozens of SEO clients improve their presence across AI platforms, we’ve created this practical guide based on what’s working in 2025.
What Exactly is an LLM?
A Large Language Model (LLM) is an artificial intelligence system trained on vast amounts of text data to understand and generate human-like language.
These models process queries and produce contextual responses by analyzing patterns in their training data and, in some cases, retrieving real-time information from the web.
Popular LLMs include:
- ChatGPT (OpenAI) - Conversational AI with web browsing capabilities
- Claude (Anthropic) - Advanced reasoning and analysis-focused AI
- Perplexity - Real-time web search with AI-powered answers
- Google Gemini - Google's multimodal AI is integrated across their ecosystem
- Microsoft Copilot - Bing-powered AI assistant
What is LLM SEO?
LLM SEO (Large Language Model SEO) is the practice of optimizing your content and online presence to get mentioned or cited by AI tools like ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, Gemini, and others.
Unlike traditional SEO, which focuses on ranking webpages in Google, LLM SEO focuses on earning visibility in AI-generated answers.
Key goals of LLM SEO:
- Get your brand mentioned in responses to relevant user questions
- Provide accurate, clear, and citation-ready content
- Build presence across trusted sources (e.g., Reddit, Wikipedia, Quora, news sites)
- Structure owned content for AI systems to understand and reuse easily
👉 Want your website to rank in AI search engines? Get your free proposal for LLM SEO services
How Does LLM Work?
The process involves several technical steps that help LLMs understand human input and generate useful, natural-sounding responses. Below are the core components explained in simple, descriptive terms.
1. Tokenization: Breaking Input Into Pieces
The first step in how an LLM processes any input is tokenization. This means the model splits a sentence into smaller parts called tokens. These tokens can be full words, parts of words, or even punctuation marks, depending on the model.
Let’s take the sentence: “Content marketing helps businesses grow.”
The LLM model might break this into tokens like:
[“Content”, “marketing”, “helps”, “businesses”, “grow”]
You can use OpenAI’s Tokenizer, a free tool to try this yourself. Below, I have shared an example of tokenization:
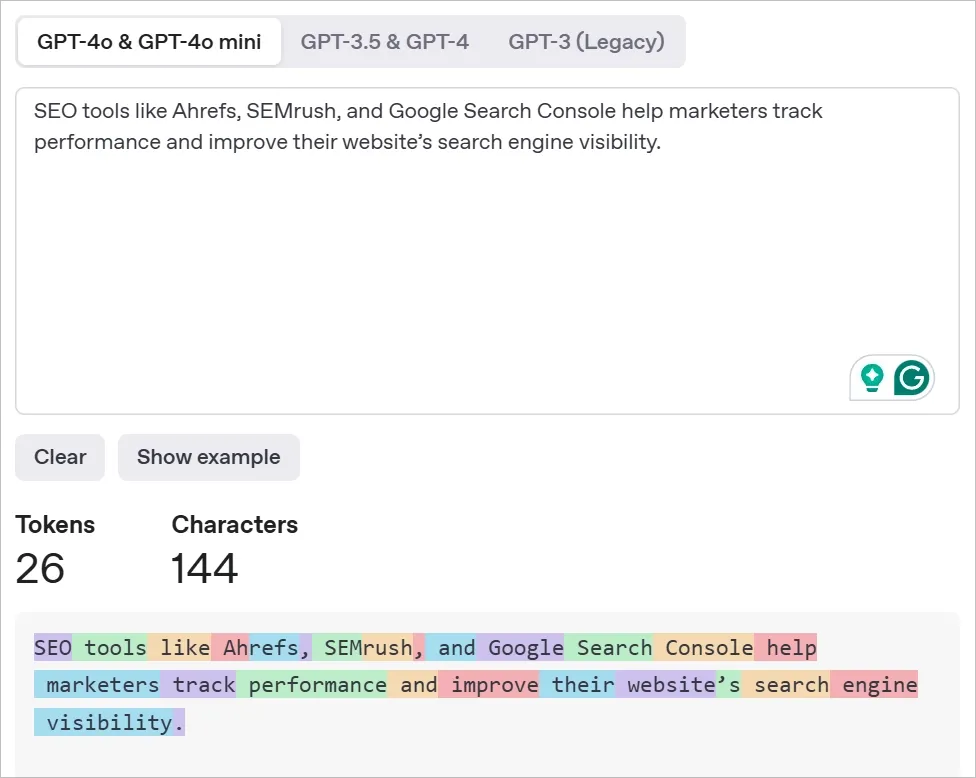
Why is this important?
Because the model doesn’t understand language the way humans do. It needs to look at each token individually to understand patterns, relationships, and structure.
2. Embedding: Turning Words Into Math
Once the text is broken into tokens, each token is transformed into something called an embedding. This is basically a set of numbers (a vector) that represents the meaning of the token in a multi-dimensional space. Think of it as translating words into math.
But this isn’t random. It’s based on how words appear together across billions of text examples.
For instance, if “SEO,” “Google,” and “keyword research” are frequently mentioned together online, their embeddings will end up very close to each other in the model’s understanding.
This step allows the LLM to understand context. Another example:
- The word “Apple” next to “iPhone” gets a different vector than “Apple” next to “fruit salad.”
- “Link building” and “backlinks” will have similar embeddings because they’re used interchangeably in SEO discussions.
Embeddings help the model know that even if someone types “optimize for search engines,” they’re talking about SEO, just in different words. This numerical mapping allows the LLM to connect meaning, not just match keywords.
3. Transformer Layers: Understanding Context with Self-Attention
Once tokens are embedded into vectors, they move through multiple transformer layers, which are the core of how LLMs understand meaning. These layers use a mechanism called self-attention. This allows the model to analyze how each word relates to others in the sentence, no matter their position.
The model doesn’t just read left to right; it dynamically decides what to focus on.
For example, in the sentence:
“ChatGPT, made by OpenAI, is a popular LLM,”
The model learns that “ChatGPT” and “OpenAI” are connected, even though “made by” is in between. Self-attention helps the model prioritize words that carry semantic weight, like product names, actions, or modifiers.
4. Prediction: Generating the Next Word
After context is understood through attention layers, the model moves into token prediction. Here, it calculates the most likely next token based on everything it has seen so far. This is done using probability distributions learned during training. It’s like asking: “Given this sentence so far, what word probably comes next?”
- For instance, if the user asks:
“What is the best SEO tool?”
The model might predict a series of tokens like:
- “There are several popular SEO tools, including Ahrefs, SEMrush, and Moz.”
The LLM draws from learned patterns across training data, millions of SEO-related pages, tools, and comparisons. The model continues predicting one token at a time until it builds a complete, human-like sentence.
5. Decoding: Converting Tokens Back Into Text
Once the LLM finishes predicting a sequence of tokens, the final step is decoding. This means converting the predicted tokens back into readable text that users can understand. The tokens are strung together and formatted into proper words, sentences, and punctuation, based on how the tokens were originally encoded.
For example, the model might generate tokens like:
- [“Content”, “marketing”, “is”, “a”, “strategy”, “used”, “to”, “attract”, “customers”, “.”]
These tokens are then decoded into:
- “Content marketing is a strategy used to attract customers.”
This decoding happens instantly within milliseconds, so the user feels like they’re having a real-time conversation. The quality of decoding affects fluency, tone, and user satisfaction.
That’s why some LLMs sound more natural than others: their decoding algorithms are better at smoothing out rough, token-level predictions into coherent outputs.
6. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): Using Real-Time Web Data
Many modern LLMs like Perplexity or Gemini use retrieval-augmented generation. This means they can search the web or their index in real-time to pull up relevant facts and cite sources.
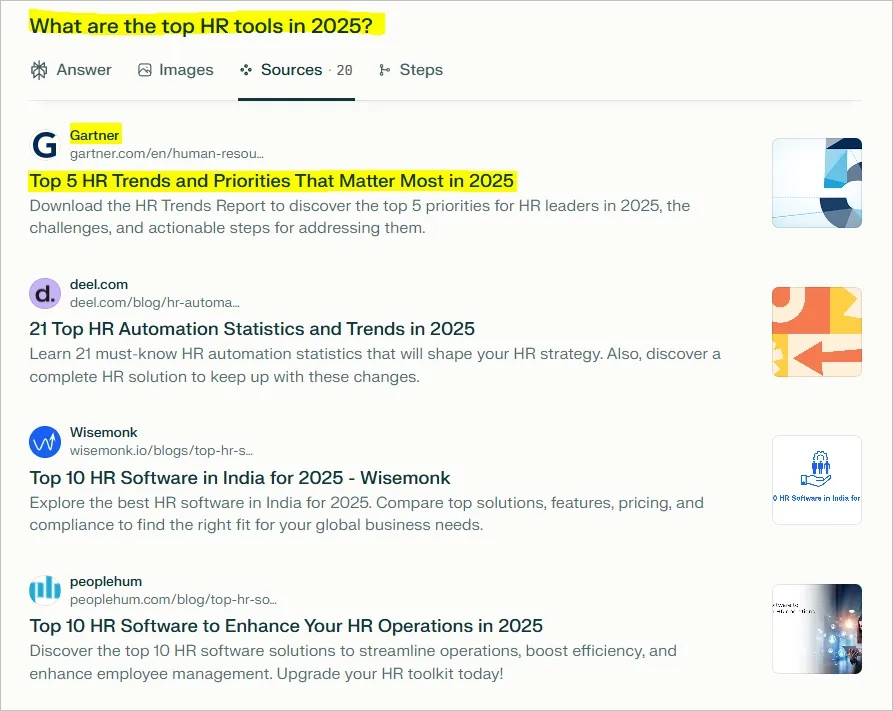
For example, if you ask Perplexity, “What are the top HR tools in 2025?”, it may fetch and summarize live content from trusted sites like G2 or Gartner, then cite them in the output.
Let me cite a real example from Perplexity showing sources behind the LLM output:
Why Getting Featured in LLMs Matters More Than Ever
1. LLMs Are the New Search Interface
People are no longer just Googling; they’re asking ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, and Claude for answers. LLMs respond with direct summaries instead of a list of links.
If your brand appears in that answer, you win attention without needing a click.
For instance, when someone asks “What are the best email marketing tools?” and ChatGPT lists your product by name, you’ve earned visibility instantly without a search engine visit.
🏆 For example, our brand Tenet is mentioned by ChatGPT when asked about the UI/UX design agencies in Dubai:
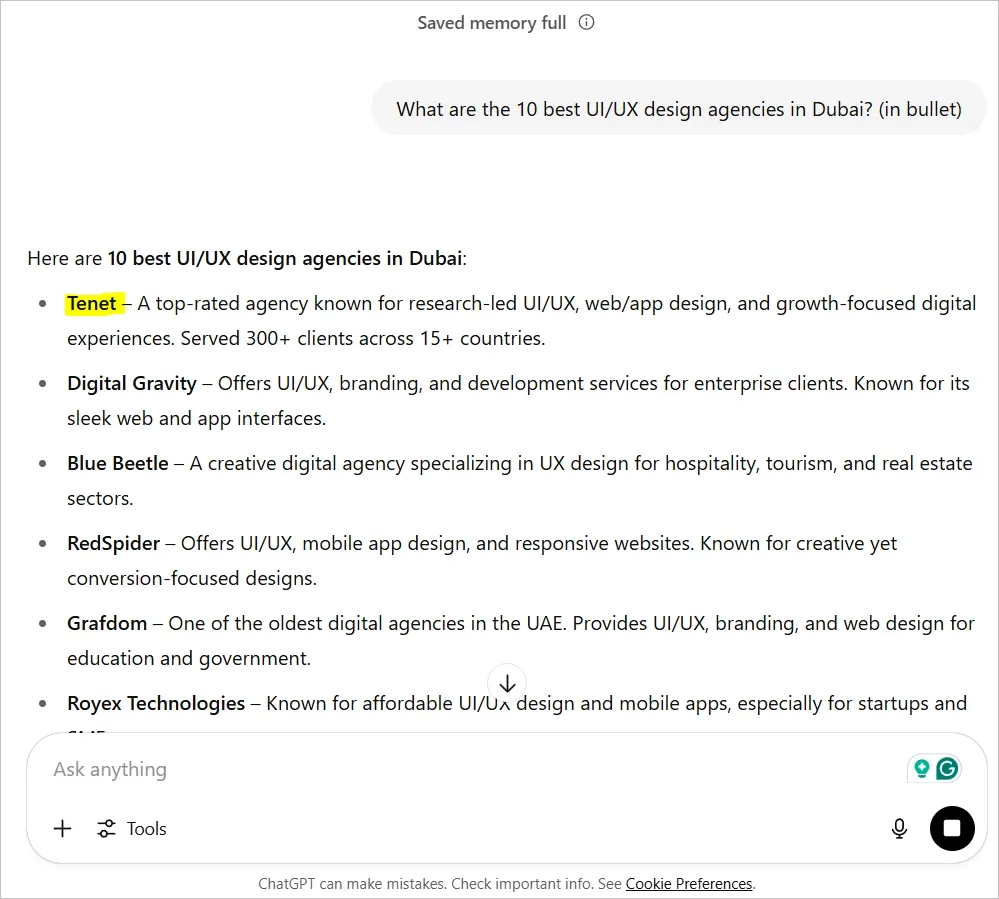
2. LLM Mentions Drive Trust and Conversions
Being cited by an AI model creates perceived authority. Users trust these summaries the same way they trust top-ranked Google results.
In many cases, they trust them even more because they appear personalized and neutral.
If your brand is named in answers like “Top alternatives to Mailchimp” or “Best platforms for HR teams in the UAE,” it builds brand credibility and influences purchase decisions.
3. LLMs Don’t Use Traditional Ranking Signals
LLMs do not care about backlinks, domain rating, or how many times you use a keyword. They look for clarity, accuracy, and citation-worthiness.
A smaller brand with well-structured, fact-rich content can now outrank a bigger site in LLM responses. That’s why getting featured is more about content quality and mention footprint than old-school SEO metrics.
4. LLMs Pull from a Broad Range of Sources
Unlike Google, which heavily favors websites with high authority, LLMs also extract content from platforms like Reddit, Quora, LinkedIn, Wikipedia, and niche blogs. That means visibility in UGC platforms and directories now plays a major role.
For example, Perplexity often cites Reddit discussions, and Gemini frequently references LinkedIn company summaries.
Here’s a live example where ChatGPT uses various sources to give you a list of top products:
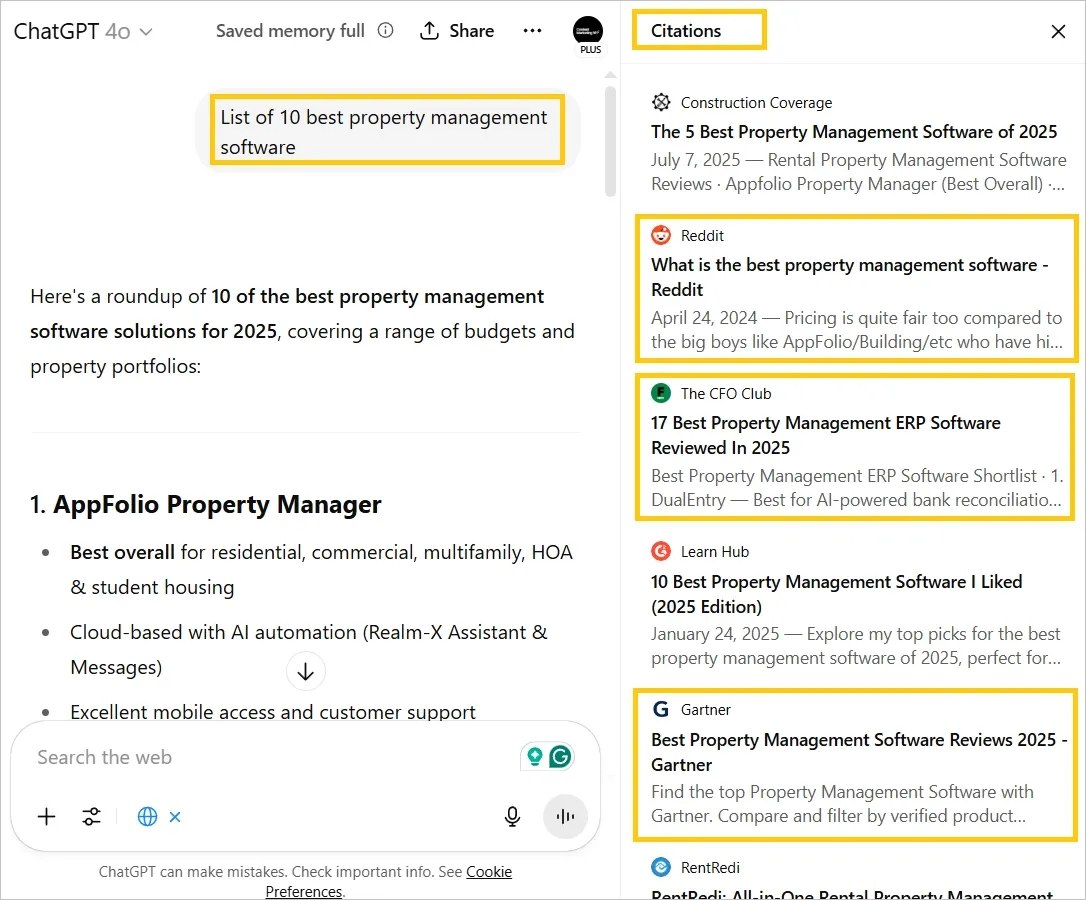
If your brand is active in those spaces, it increases your chances of being pulled into responses.
5. Visibility Is Dynamic and Model-Driven
LLMs update regularly, and their knowledge changes with each version. Even if you appear in an answer today, you might be gone tomorrow.
New content, user feedback, and fine-tuning affect what’s included. That means you need to keep reinforcing your presence across trusted platforms consistently. Static SEO alone won’t guarantee staying power in LLM answers.
6. Following Traditional SEO Alone Is Not Enough
There’s a common belief that if you do great SEO, LLMs will automatically pick your site. This is only partially true. Traditional SEO helps, but it doesn’t cover external mentions, UGC presence, or structured brand facts. To rank in LLMs, you need to go beyond search rankings.
Focus on creating content and citations that are ready for machines to quote, not just humans to read.
Here’s a Step-by-Step Framework to Get Featured in LLMs
Step 1: Conduct a Comprehensive LLM Audit
Start by evaluating your brand's current presence across major LLM platforms. This involves testing your brand visibility across different AI chatbots, as each one operates on distinct principles and training data.
Create a comprehensive list of LLM platforms where you want to establish a presence, such as ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, Gemini, and others relevant to your industry.
Begin by testing basic brand recognition queries like:
- “What is [your brand name]?”
- “Tell me about [your company].”
The goal is to understand how LLMs recognize and describe your brand as an entity. Do these models provide accurate information about your business—its services, USPs, locations, and other key details?
For example, here’s the response we got when searching for the brand Tenet as a UI/UX agency:
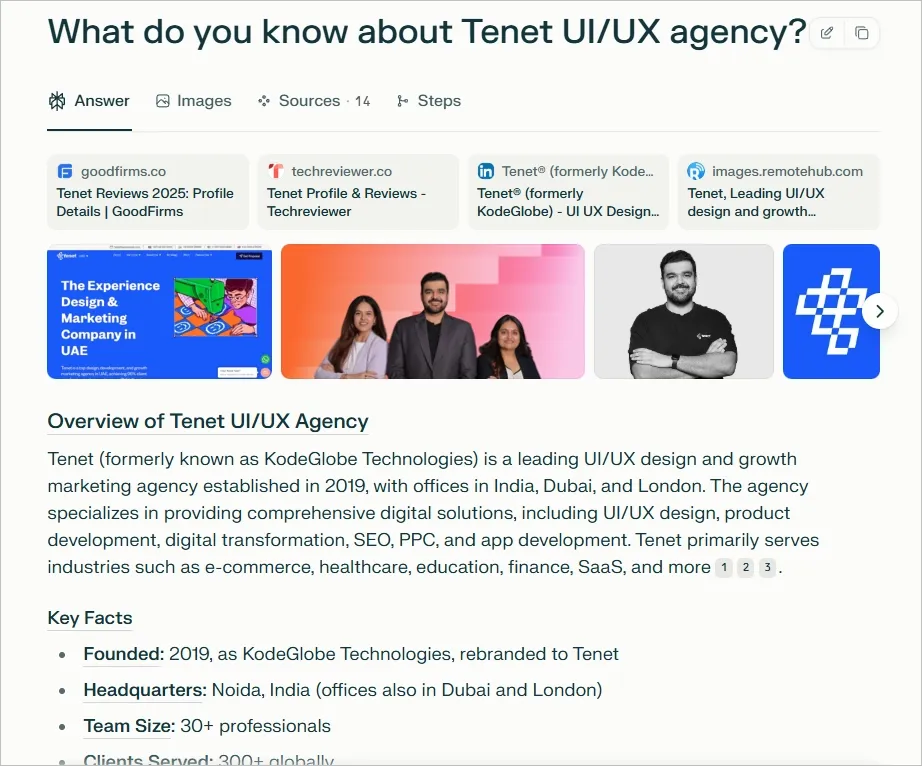
This response includes details about the brand, its services, office locations, and even testimonials.
After running a similar query for your brand, you’ll gain a clearer picture of what information LLMs currently hold about you.
Write down the LLM responses. Check if your brand is mentioned, how it is described, and whether the information is correct and well-positioned.
Next, expand your testing to category-specific queries that potential customers might use.
Test phrases like "What are the best [your product category] tools?" or "Top [your industry] solutions for small businesses."
Pay careful attention to whether your brand appears in these recommendation lists and, if so, at what position and with what description.
Document all findings in a structured format, creating a comprehensive snapshot of your current LLM visibility. This audit should include screenshots, exact quotes from LLM responses, and an analysis of how your brand is positioned relative to competitors.
Step 2: Analyze Source Attribution and Citation Patterns
LLMs draw information from diverse sources, and understanding these sources is critical for developing an effective optimization strategy.
Many LLMs, particularly those using Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems like Perplexity, provide citations and source links with their responses. Analyze these citations carefully to understand where information about your brand and competitors is being sourced.
Create a comprehensive inventory of source types that LLMs frequently cite in your industry.
Common sources include:
- company websites
- product landing pages
- social media profiles
- directory listings
- review platforms
- news articles/ blog posts
- Wikipedia pages
- user-generated content from platforms like Reddit and Quora
Each source type serves different purposes and reaches LLMs through different pathways.
Pay special attention to the specific pages and content formats that get cited most frequently. Are LLMs pulling from FAQ pages, product descriptions, about pages, or third-party reviews?
Notice patterns in content structure, such as whether cited content uses specific heading hierarchies, includes data and statistics, or follows particular formatting conventions.
Here’s a scorecard you can use to document your LLM responses for commercial search queries:
This reverse engineering process reveals the specific content and platforms that carry the most weight in LLM training and retrieval systems.
Another example is a list we created of competitors dominating LLM results for the query: "best property management software."

Step 3: Optimize Foundation Content for LLM Consumption
Your owned digital properties serve as the foundation for LLM's understanding of your brand. These include your website homepage, product pages, about page, FAQ section, and social media profiles.
Start with your website's core pages, ensuring they clearly and concisely explain what your company does, who you serve, and what problems you solve. LLMs favor content with clear, direct language and logical structure.
💡 TIP: Avoid marketing jargon and complex sentence structures that can confuse natural language processing systems. Instead, use simple, declarative sentences that directly answer common questions about your brand.
- ✔️ Good example: We help small businesses manage rental properties with easy-to-use software.
- ❌ Poor example: Our cutting-edge platform is designed to revolutionize property management through a comprehensive suite of features that empower users in unprecedented ways.
Create a comprehensive FAQ page that addresses all common questions about your brand, products, and industry.
This page should be structured as a clear question-and-answer format that directly addresses the types of queries users might ask LLMs.
Answer questions like "What is [your product]?", "How does [your service] work?", "Who should use [your solution]?", and "What makes [your brand] different from competitors?"
Here’s one example where the brand has created an FAQ page answering all branded questions:

As a result, Perplexity is using this FAQ page as a source to answer a branded question, which can affect their brand reputation.

Also, update your social media profiles, particularly LinkedIn, to include clear, keyword-rich descriptions of your business.
These profiles often get indexed and can be cited by LLMs, so ensure they accurately represent your brand positioning and key value propositions.
A highly effective strategy for LLM-powered results is to build a factual, machine-readable foundation of information about your brand.
AI Assistive Engines like ChatGPT and Google's AI Overviews and AI Mode prioritize understanding, which they build by connecting facts from across the web. If your digital footprint is confusing, the AI will lack the confidence to feature you accurately.
The most practical way to do this is by defining your core narrative using semantic triples (Subject-Predicate-Object). The predicate is the relationship that connects the subject and object, most often a verb. For example, explicitly state facts like:
"Kalicube (subject) is a (predicate) digital branding consultancy (object)."
"Kalicube (subject) specializes in (predicate) helping entrepreneurs (object) with their personal brand in Google and AI."
Publish these foundational facts on an authoritative "Entity Home," like your About Us page, and ensure this information is consistently echoed across trusted third-party sources. With this consistent "Digital Brand Echo", you educate the algorithm, establishing the Understandability it needs to confidently and correctly recommend your brand.
Step 4: Develop Strategic Content for Topic Authority
LLMs associate brands with topics based on the proximity and frequency of mentions across their training data. To increase your chances of being mentioned in relevant conversations, you must establish clear topical authority through strategic content creation.
This involves creating comprehensive, authoritative content that positions your brand as the definitive source for specific concepts or solutions.
Identify the core topics and concepts where you want to establish authority.
These should align with your business objectives and represent areas where potential customers seek information.
Rather than trying to compete on broad, highly competitive topics, focus on specific niches where you can become the canonical source of information.
Here’s a rough example showing the core topic (UI/UX service in this case), branches, and individual topics under each branch:

Here are some practical SEO content strategies for LLM ranking:
Structured FAQs and listicles unlock LLM search visibility
In my work with LLM-powered search results, I've found that structured FAQ content delivers exceptional visibility. When you strategically address common customer questions on your website and implement proper FAQ schema markup, you're essentially serving up perfect content packages for AI systems to cite.
These platforms are designed to match queries with clear, authoritative answers, and well-structured FAQs align perfectly with their retrieval mechanisms.
Beyond FAQs, listicle articles consistently perform well in LLM results. I've had success with a targeted outreach approach: search for topics like "best CRM tools" or "best marketing agencies in [specific city]" in ChatGPT or similar platforms, analyze which sources they're referencing, then connect with those publishers for backlink opportunities. This substantially increases your chances of being featured in AI-generated responses.
Product-led content will replace educational SEO strategy
Within the next years, the value of "educational content" will drop to nearly zero. Google and LLMs will answer informational queries directly in the search interface or app. And so there is little incentive to keep creating such content.
So, I'd suggest moving away from creating wiki-style content and recommend doubling down on product-led content at the bottom of the funnel to reach people who are ready to buy.
Product-led content makes it clear to searchers (and LLMs) why your product is the best fit for their specific situation. Even ChatGPT has to mention certain brands when users ask for concrete recommendations.
And if you're creating the right content, LLMs will actively recommend and sell your products for you. Classic formats that drive visibility in LLMs and convert well are product pages, listicles, alternative posts, industry pages, product comparisons, etc.
First, start creating that content for your website, and then look at how you can distribute it on external platforms as well.
By setting up a basic prompt tracking in tools such as peec.ai, you can find the most cited resources and either create similar content yourself, or find ways to influence that source and get your brand into the answers of the LLMs.
Step 5: Execute Targeted PR and Media Outreach
Building Topical Associations Through Media Coverage
Public relations and media coverage play a crucial role in LLM optimization because they create authoritative third-party associations between your brand and relevant topics.
LLMs often reference news articles, press releases, and other media coverage when generating responses about companies and industries.
Develop a strategic PR campaign that focuses on establishing your brand as an authority in specific topic areas. This might include announcing new product features, sharing industry insights, participating in relevant conversations, or positioning your executives as thought leaders.
👉 Here are some action items to follow:
- Develop a PR strategy focused on building authority in your niche topics.
- Publish newsworthy updates like product launches, feature rollouts, or company milestones.
- Pitch industry insights or expert opinions to relevant journalists and editors.
- Position founders or executives as thought leaders through interviews and bylined articles.
- Target high-authority publications likely to be in LLM training data (e.g., TechCrunch, Forbes, industry blogs).
- Earn coverage that includes brand mentions, quotes, and expert commentary.
- Create high-value, linkable assets (e.g., original research, reports, whitepapers).
- Promote those linkable assets to journalists and industry blogs for citation opportunities.
- Track media mentions using tools like Google Alerts or Brandwatch.
- Monitor changes in LLM responses after PR coverage to measure impact.
There's a cheat code right now for LLM-powered results: press releases.
Write a short article about your brand, drop in the exact keywords you want to be associated with, like 'headache-free coffee + [your brand]', and push it out through a cheap $5 distribution service on Fiverr.
Once those press releases land on high-authority sites, LLMs will start citing them.
Example: 'According to APNews.com, XYZ Brand has some of the best headache-free coffee.'
Step 6: Leverage User-Generated Content Platforms
User-generated content platforms like Reddit, Quora, Stack Overflow, and industry-specific forums represent valuable sources of information that LLMs frequently reference.
These platforms are particularly important because they contain authentic conversations and recommendations from real users, which LLMs often treat as authoritative sources.
Identify the most relevant subreddits, Quora spaces, and forum communities where your target audience discusses problems that your product or service solves.
You can use Audience Research Assistance (a free tool) to find relevant threads from platforms like Reddit, Quora, and Substack.
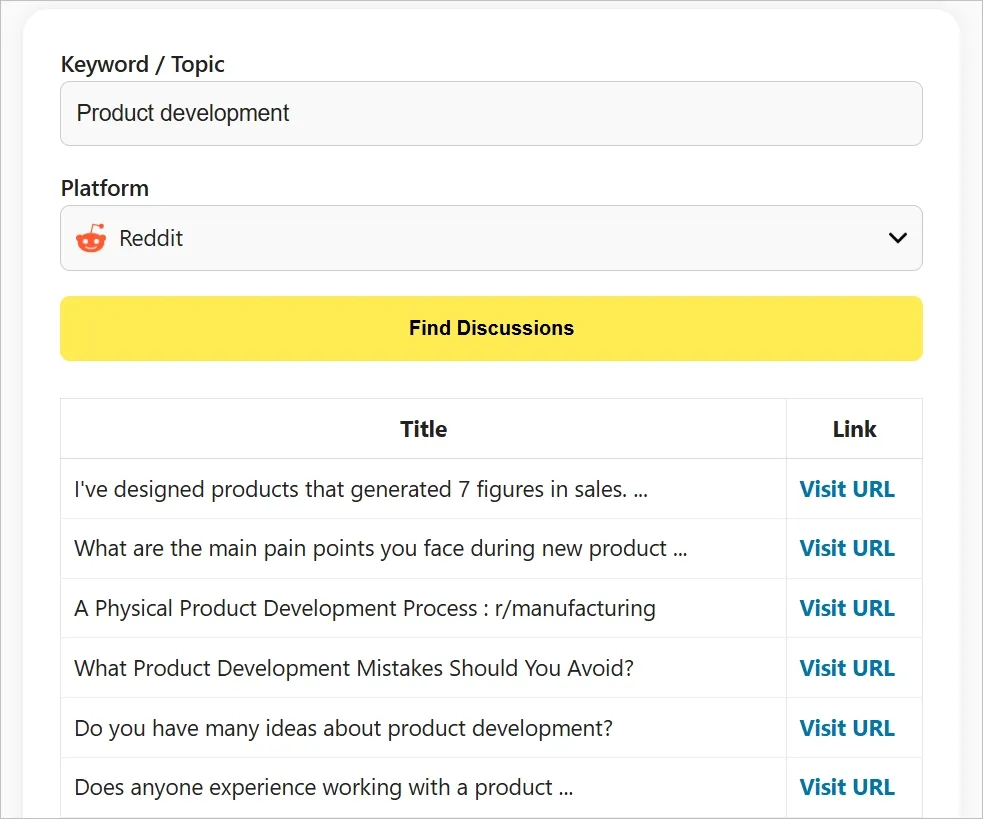
Just enter your core topic and select the platform (Quora, Reddit, LinkedIn, Hacker News, etc.) you want to analyze. The tool will show you a list of posts or threads related to your topic, which you can download as a CSV file.
Next, participate authentically in these communities by providing helpful answers, insights, and solutions. Avoid overtly promotional content, instead focusing on building genuine value and establishing your expertise.
Create comprehensive answers to common questions in your industry. These detailed responses should provide substantial value while naturally mentioning your brand where appropriate. Focus on being helpful first, with brand mentions serving as natural extensions of your expertise rather than forced promotional content.
Track how your community engagement correlates with changes in LLM mentions. This helps you understand which platforms and types of engagement are most effective for improving your AI visibility.
Step 7: Optimize for Search Engine Visibility
Traditional search engine optimization remains crucial for LLM visibility because many AI systems use search engines as sources for real-time information retrieval. Strong organic search performance can significantly improve your chances of being mentioned and cited by LLMs.
In fact, brands on page 1 of Google are more likely to be mentioned by LLMs (~0.65 correlation). Bing rankings also help but less strongly (~0.5–0.6), based on a recent study by SeerInteractive.
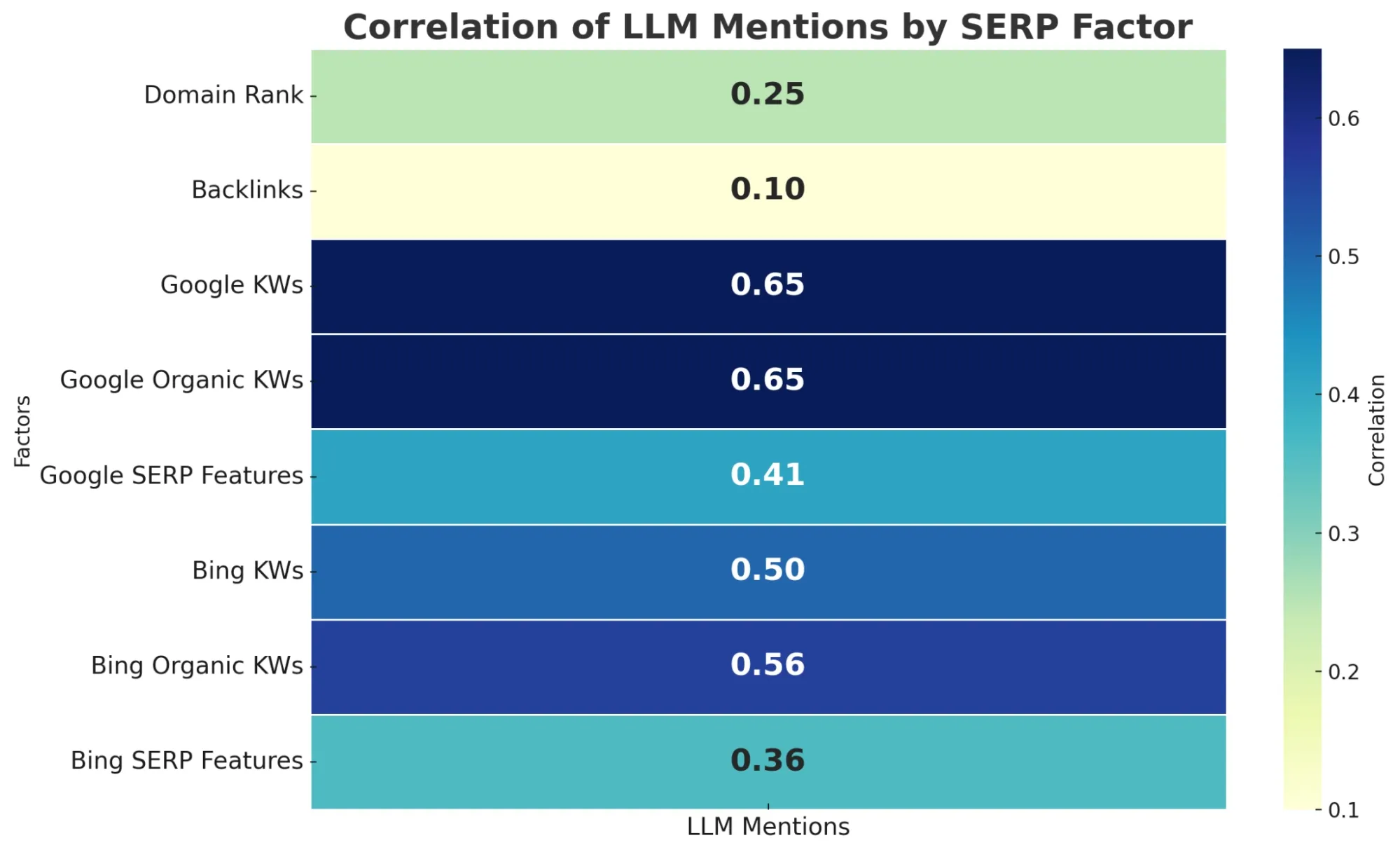
Focus on ranking for product-category keywords and bottom-of-funnel search terms that potential customers use when seeking solutions like yours.
These are often the same queries that users ask LLMs, so strong search visibility can translate into improved AI mentions.
Create comprehensive, authoritative content that targets specific long-tail keywords and questions. This content should be optimized for both traditional search engines and LLM consumption, with a clear structure, semantic markup, and in-depth coverage of topics.
Build high-quality backlinks from authoritative websites in your industry. These links not only improve your search rankings but also increase the likelihood that your content will be included in LLM training data and cited in AI responses.
Step 8: Monitor and Measure LLM Performance
Measuring LLM performance requires a systematic approach to tracking mentions, citations, and referral traffic from AI platforms.
Unlike traditional SEO, where rankings are clearly defined, LLM performance measurement involves tracking brand mentions, context, and positioning across various AI platforms.
You can do that manually, with the help of a scraping algorithm, or with specialized tools like AI Visibility Tracker by SE Ranking. A tool like this will run your prompts on a schedule, scrape the results, and present data on your brand and site’s presence across five major LLMs, changes in positions for the tracked prompts, and more.
Set up regular monitoring of your brand mentions across major LLM platforms. Test consistent queries weekly or monthly to track changes in how your brand is mentioned and positioned. Document these responses with screenshots and detailed notes about context and positioning.
Monitor referral traffic from AI platforms using web analytics tools. Track visits from domains like chat.openai.com, perplexity.ai, and claude.ai to understand how AI mentions translate into actual website traffic and conversions.
Track the sources and citations that LLMs use when mentioning your brand. This helps you understand which of your content and PR efforts are most effective for improving AI visibility.
Step 9: Continuously Adapt and Optimize
The LLMs are rapidly evolving, with new models, platforms, and capabilities emerging regularly. Successful LLM optimization requires continuous adaptation and refinement of your strategy based on performance data and industry changes.
Stay informed about changes in model capabilities, training data, and citation behavior. Experiment with new content formats and platforms early to gain a competitive edge.
Regularly track performance and refine your approach based on what works best for your industry and use case.
👉 Explore our SEO services by country:
LLM Optimization vs. Traditional SEO: Are There Any Key Differences?
1. Purpose: Ranking Pages vs. Getting Quoted in Answers
Traditional SEO focuses on ranking a specific page in the search engine results for a keyword query. The goal is to get users to click on your link. In contrast, LLM optimization is about getting your brand or content mentioned directly in the model’s answer.
For example, while traditional SEO aims to rank your article on “best CRMs for startups,” LLM optimization ensures your brand name shows up in the AI's response when asked, “Which CRM should a startup use?”
2. Ranking Signals: Backlinks vs. Clarity and Citability
Google uses backlinks, page authority, mobile-friendliness, and other signals to rank content. LLMs don’t rely on these signals in the same way. They prioritize clear, factual, citation-ready information.
For instance, a site with a DA of 25 can appear in a Gemini or Perplexity answer if it includes concise, structured content like “X is a free tool that helps with Y” written in simple language.
The focus shifts from building links to being linguistically and semantically useful.
3. Content Style: Keyword Targeting vs. Natural Language
SEO content is often written around a specific keyword strategy, placing the primary keyword in titles, headers, and alt tags. But LLMs prefer natural, conversational language. The content should answer real questions clearly and directly, even without keyword stuffing.
For example, instead of writing “best time tracking software in 2025,” LLM-optimized content might say, “TimeCamp and Toggl are two popular tools used by remote teams to track work hours and improve productivity.”
4. Sources: Controlled Websites vs. Multi-Platform Ecosystem
In traditional SEO, your owned assets (websites, blogs, landing pages) do most of the work. LLMs, however, pull data from a much wider ecosystem: Reddit threads, Quora answers, GitHub repos, LinkedIn bios, press mentions, Wikipedia, and even YouTube descriptions. This means your brand needs to show up across platforms, not just rank well on Google.
In fact, if your competitor is getting cited from a G2 review or a Reddit upvoted comment, you’ll need to be there too.
5. Structure and Formatting: Schema Markup vs. Answer-Friendly Sentences
Schema helps Google understand your site’s structure (e.g., FAQs, HowTos, Reviews). LLMs, on the other hand, prefer readable, declarative statements they can quote or rephrase easily.
Instead of using bullet points alone, write summary-style sentences like “FreshBooks is an accounting tool designed for freelancers.”
This makes it easier for the model to lift and adapt your text during response generation.
6. Optimization Mindset: Static vs. Dynamic Discovery
Traditional SEO relies on long-term page authority building. Once a page is optimized, it gradually climbs the SERPs as it gains backlinks, engagement signals, and crawl frequency over time.
LLM optimization requires a more dynamic approach. Mentions are not guaranteed to stick, and models constantly change based on updates and retraining.
So, your strategy must involve constant citation building, FAQ revisions, entity clarity, and source diversification to stay relevant in LLM-generated content.
Learn about SEO vs Google Ads: Which one to choose?
Final words: Building Long-Term LLM Success
Optimizing for LLM visibility requires a comprehensive, long-term approach that combines traditional digital marketing tactics with new strategies specifically designed for AI systems. Success depends on consistently creating high-quality, authoritative content while building genuine topical authority and community engagement.
The key to LLM optimization is understanding that these systems reward authenticity, authority, and genuine value creation. Unlike traditional SEO, where tactics and technical optimizations can sometimes overcome content quality issues, LLM optimization requires genuine expertise and sustained effort to build real authority in your field.
By following this comprehensive framework and continuously adapting to the evolving LLM landscape, you can build sustainable visibility in AI-generated responses and position your brand for success in the age of artificial intelligence.
Want your website to rank in AI search engines? Get a free LLM SEO proposal plan.
Want your website to rank in AI search engines? Get a free LLM SEO proposal plan.

Got an idea on your mind?
We’d love to hear about your brand, your visions, current challenges, even if you’re not sure what your next step is.
Let’s talk