Ecommerce Mobile App Development: Types, Cost, & Timeline
Share
Share

Get a quick blog summary with
Building an e-commerce mobile app isn’t just about selling— it’s about creating an experience your customers love.
In this guide, you’ll learn the types of e-commerce apps, key features users expect in 2025, and the step-by-step process to develop a high-converting app.
Whether you're planning your first app or upgrading an existing one, this blog gives you the insights to take action with confidence.
What is e-commerce mobile application development?
E-commerce mobile app development is the process of building mobile applications that allow users to browse, shop, and pay for products or services directly from their smartphones or tablets.
These apps are built specifically for platforms like Android and iOS to deliver a smooth, on-the-go shopping experience.
It goes beyond just putting your website on an app, it involves designing fast, user-friendly, secure, and conversion-focused mobile interfaces that can handle product listings, payment gateways, order tracking, and more.
👉 Explore our eCommerce services:
- Ecommerce UI/UX Design Services: Improves user experience and conversions with clean, intuitive, and mobile-optimized designs.
- Ecommerce App Development: Builds secure, fast, and scalable ecommerce apps tailored for seamless mobile shopping.
- Ecommerce CRO Agency: Increases sales and reduces drop-offs through data-driven conversion rate optimization strategies.
What are the types of e-commerce mobile apps?
E-commerce mobile apps come in various forms, each tailored to different business models and customer needs. Understanding the main types helps you choose the right approach to maximize reach, engagement, and sales.
Let’s explore the key categories along with real brand examples that demonstrate their unique strengths.
1. B2C (Business-to-Consumer): Selling Directly to Shoppers
B2C apps connect businesses directly with everyday shoppers, focusing on convenience, speed, and personalized experiences. Imagine browsing thousands of products with a few taps and getting what you want delivered fast - that’s B2C ecommerce. These apps thrive on ease of use, smart recommendations, and seamless checkout.
Example:
Amazon is the king of B2C apps, offering everything from books to groceries with lightning-fast delivery and features like 1-Click ordering and personalized suggestions.
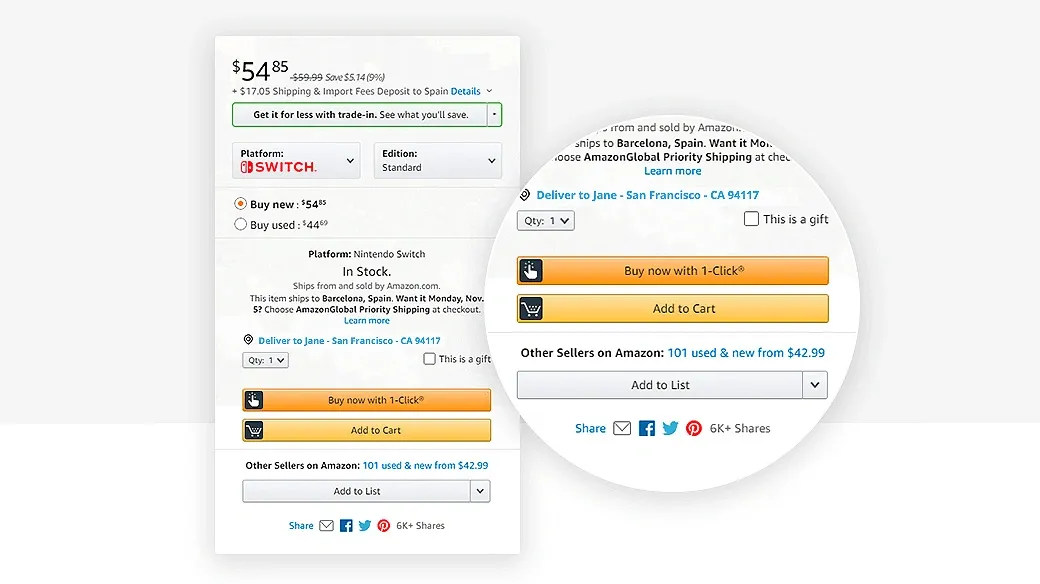
2. B2B (Business-to-Business): Powering Wholesale & Partnerships
B2B ecommerce apps cater to businesses purchasing in bulk or managing supply chains. These platforms prioritize features like custom pricing, bulk orders, and account management, helping companies streamline complex purchases and build long-term partnerships.
Example:
Alibaba connects wholesalers and manufacturers worldwide, offering tailored pricing, RFQ (Request for Quotation) tools, and logistics integration that simplify global trade.

3. C2C (Consumer-to-Consumer): Enabling Peer-to-Peer Commerce
C2C apps empower users to sell or trade items directly with each other. These platforms build trust with ratings, messaging, and secure payments, creating vibrant marketplaces where anything from used gadgets to vintage clothes can find a new home. For a deep understanding, see building a food delivery app like Zomato explained.
Example:
eBay revolutionized peer-to-peer selling with auctions and fixed-price sales, while OLX focuses on local buying and selling, enabling users to quickly find deals nearby.

4. Marketplace: A One-Stop Shop for Diverse Sellers
Marketplace apps aggregate multiple sellers under one roof, allowing users to compare products, prices, and reviews all in one place. These platforms handle payments, logistics, and customer service, letting sellers focus on what they do best—selling.
Example:
Etsy offers a unique marketplace for handmade and vintage goods, helping artisans reach millions of buyers worldwide while managing transactions and shipping.
👉 Interested in a similar model? Learn how to develop a marketplace app like Airbnb.

5. D2C (Direct-to-Consumer): Brands Building Customer Loyalty
D2C apps allow brands to cut out the middleman and connect directly with customers, offering exclusive products, personalized experiences, and loyalty perks. This approach builds stronger brand loyalty and better insights into customer preferences.
Example:
The Nike App offers exclusive product launches, personalized workout plans, and rewards, creating a vibrant community around the brand.

Visual of the Nike app showing the personalized workout plans
Choosing the right type of e-commerce mobile app depends on your
- business goals,
- target audience, and
- product offerings.
Each app type brings its own strengths and caters to different customer behaviors.
To help you decide which e-commerce mobile app suits your needs best, here’s a quick comparison of the main types, their ideal use cases, and examples of top brands leading the way.
A table representing the types, key features & typical challenges of e-commerce apps.
What are the benefits of building a mobile app for your e-commerce store?
1. Higher Conversion Rates
Mobile apps tend to convert better than mobile websites. In fact, shopping apps average a 3.5% conversion rate, while mobile websites see around 2%.
With stored user data, smoother navigation, and fewer friction points, apps reduce drop-offs, especially at checkout. If you're seeing good traffic but low purchases, moving your customers to an app experience might be the best next step.
In fact, cart abandonment rates are notably lower on apps than on mobile websites, leading to more completed purchases and increased revenue.
👉 To further optimize your sales funnel, consider our Ecommerce CRO services to boost your sales.
2. Enhanced Customer Engagement and Retention
App users spend over 200 minutes a month shopping, compared to barely 11 minutes on mobile websites. That’s more time to re-engage, recommend products, and increase average basket size.
Plus, you can build habits with in-app offers or loyalty rewards. If repeat purchases are a weak spot, your mobile app gives you a direct, distraction-free channel to bring them back.
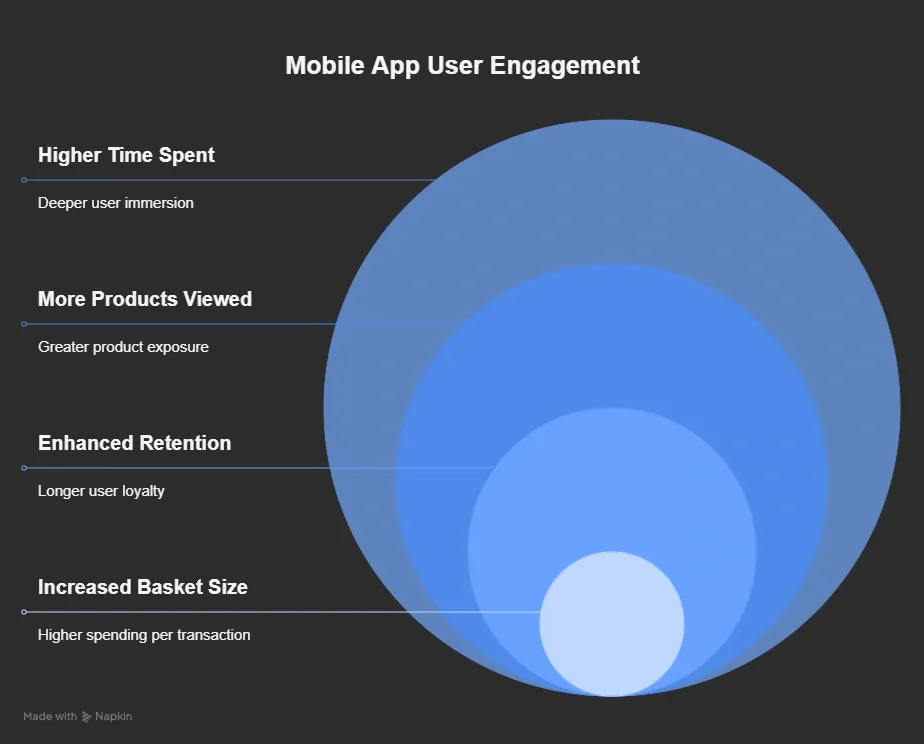
3. Personalization Increases Revenue
Apps give you better control over the user journey. You can track behavior and offer suggestions when they actually make sense, like nudging someone after they revisit a product twice.
Brands that invest in personalized shopping experiences can grow revenue by 6–10% on average. But more than that, it builds trust. When your app feels relevant, not random, customers are more likely to engage, add to cart, and return without relying on retargeting ads.
4. Offline Access Enhances User Experience
Providing offline access through mobile apps ensures that users can interact with the brand even without an internet connection, leading to increased engagement and potential sales.
Offline access might seem like a small perk, but it quietly improves user stickiness. It lets customers browse wishlists, saved products, or old carts without internet. Especially useful during travel or in low-signal zones, where mobile websites just won’t load.
An app that works when the web doesn’t, keeps you top-of-mind, and gives customers one more reason to stay inside your ecosystem.
5. Easier Use of Phone Features
Your app can let customers use their phone camera to scan a barcode, find products based on location, or log in with Face ID for secure logins, enhancing the overall shopping experience. These features may seem small, but they shave off precious seconds, and those seconds reduce drop-off.
If you're looking to improve the post-click experience, these native features help users complete tasks faster and build trust while doing it.
👉 If you’re interested in location-based services, review the essential steps to create a ride-sharing app like Uber.
What are the must-have ecommerce mobile application features in 2025
Below are the key features every e-commerce mobile app should have in 2025.
1. Bottom Navigation Menu Bar
Users naturally hold their phones so their thumbs rest near the bottom of the screen. Placing essential navigation buttons like Home, Search, Cart, and Profile at the bottom makes the app easier to use.
This reduces the need to stretch fingers or hunt through menus, which lowers frustration.
When navigation is simple and fast, users browse more products and spend more time in the app. That longer engagement often leads to higher sales and better customer retention. If your app still hides key options in hard-to-reach places, it can slow down or lose potential buyers.
Example:
Amazon’s mobile app uses a clear bottom navigation bar with icons for Home, Deals, Orders, and Cart, ensuring users can quickly switch to where they want. This simplicity supports faster shopping journeys and reduces friction.
Image showing Amazon’s mobile app using a clear bottom navigator:

2. Guest Checkout & Multiple Payment Options
19% of shoppers abandon their carts because they’re forced to create an account before buying. Offering a guest checkout option removes this barrier and lets customers complete purchases faster. Along with this, providing a variety of payment options like PayPal, Apple Pay, Google Pay, UPI, or Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) meets the different preferences and needs of customers across regions.
The easier and quicker the checkout feels, the less chance customers will leave without buying. This flexibility often leads to more completed sales and happier customers.
👉 If you’re targeting Android users, explore our Custom Android app development services.
Example:
Flipkart’s app supports guest checkout and multiple payment methods like UPI and mobile wallets, catering to India’s varied payment landscape. This approach lowers barriers and boosts completed sales.

Image showing multiple payment options given by Flipkart.
3. Multilingual Support
Your store could have customers from many countries, and offering content in their native language makes a big difference. Studies show that 64% of consumers are willing to pay more when a brand speaks their language.
Beyond just translating the interface, product descriptions, reviews, and FAQs should also be localized. Allow users to pick their language or detect it automatically based on device settings or location.
When customers feel understood, trust increases, and they are more likely to buy and come back.
Example:
AliExpress supports 15+ languages and local currencies, significantly increasing trust and conversion across Asia, Europe, and Latin America.
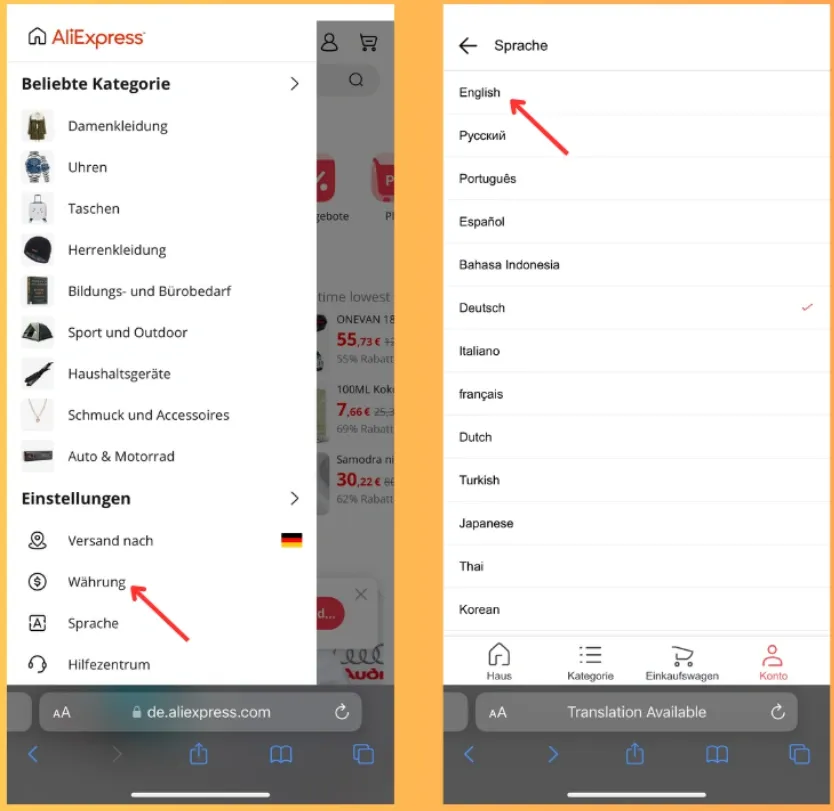
This picture shows how AliExpress provides 15+ languages to the app users
4. One-Click Chat Support
Customers often have questions about products, shipping, or returns while shopping. Having real-time chat support right in the app answers these doubts immediately and reduces hesitation.
Providing AI chatbots for common questions, combined with easy access to live agents for more complex issues, keeps customers engaged and reduces drop-offs. This quick help encourages shoppers to finish their purchases and can improve repeat buying by building trust.
Example:
Zalando provides live chat on product pages, enabling users to ask about size availability or return policy mid-browse, drastically reducing drop-offs.

Image showing Zalando’s AI-powered chat support
5. Advanced In-App Search
When shoppers open an app, they usually know what they want. If they can’t find it quickly, they’ll leave.
A strong search function helps guide users to the right products, even if they aren’t sure what exactly they want. Features like autocomplete suggestions, recent searches, and voice input make finding products faster and easier.
Adding image search is especially useful for categories like fashion or home decor, where users can upload a photo to find similar items. Filters for price, brand, size, and shipping speed help shoppers narrow results and make decisions faster.
Example:
eBay enables visual and voice search, allowing shoppers to upload an image and find similar items. It shortens the path from discovery to checkout
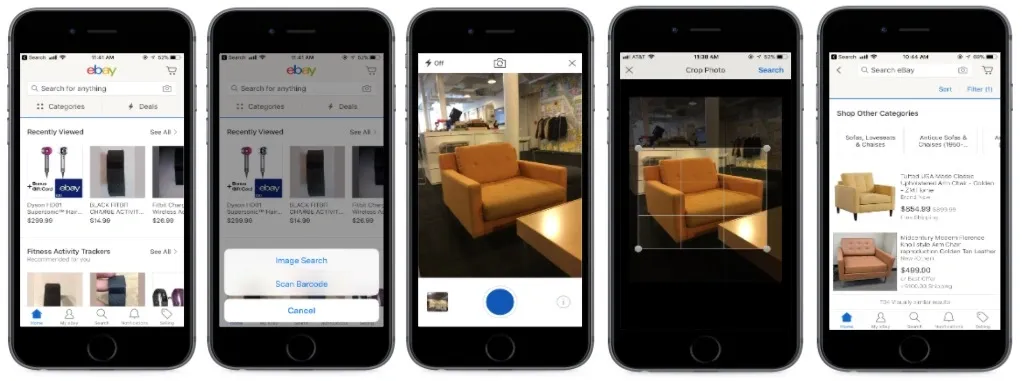
Image showing how eBay enables visual search
6. Personalized Recommendations
Personalization makes shopping feel more relevant and less like marketing.
Apps that analyze browsing history, past purchases, and wishlists can suggest products users actually want. This tailored approach encourages shoppers to explore more and often increases how much they spend.
Personalized homepage banners, carousels, and notifications keep users engaged with products that matter to them. In fact, personalized product recommendations have been shown to increase average order value by 11%.
Example:
Etsy shows tailored suggestions as soon as a user logs in, based on recent views and similar users’ preferences, boosting basket size and time spent in-app.
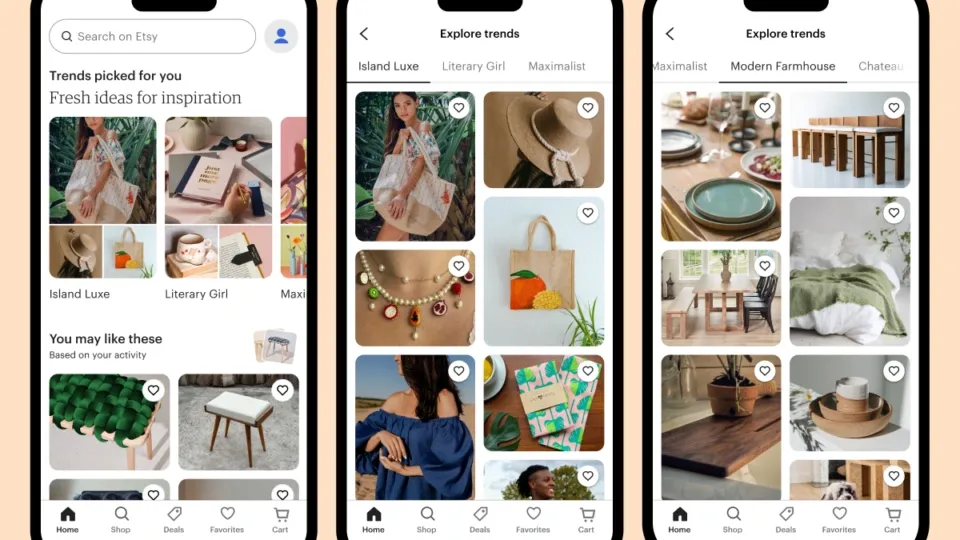
The image shows Etsy’s providing personalized recommendations and trends to the users
7. Secure User Authentication & Account Management
With growing cybersecurity concerns, security is a top concern for online shoppers. Features like biometric login and two-factor authentication (2FA) in the app can help protect user data and build trust.
When shoppers feel confident their information is safe, they’re more likely to return and shop regularly.
Also, easy account recovery and options to switch between accounts smoothly improve the overall user experience, reducing frustration and keeping users active.
Example:
Apple Store’s app uses Face ID for seamless login. It removes the need to remember complex passwords and increases the likelihood of repeated sessions.
8. Augmented Reality (AR) Integration
Why it matters:
Augmented Reality (AR) lets customers visualize products in their own space before buying, which bridges the gap between online and physical shopping.
This helps shoppers make better decisions and feel more confident, reducing returns. For example, customers can see how furniture fits in a room or try on virtual makeup. Even studies show that around 40% of consumers are willing to pay more if they can test products using AR, showing its strong impact on buying behavior.
Example:
IKEA Place lets users drop 3D furniture models into their room using their phone camera. It reduces return rates and increases buyer confidence significantly.
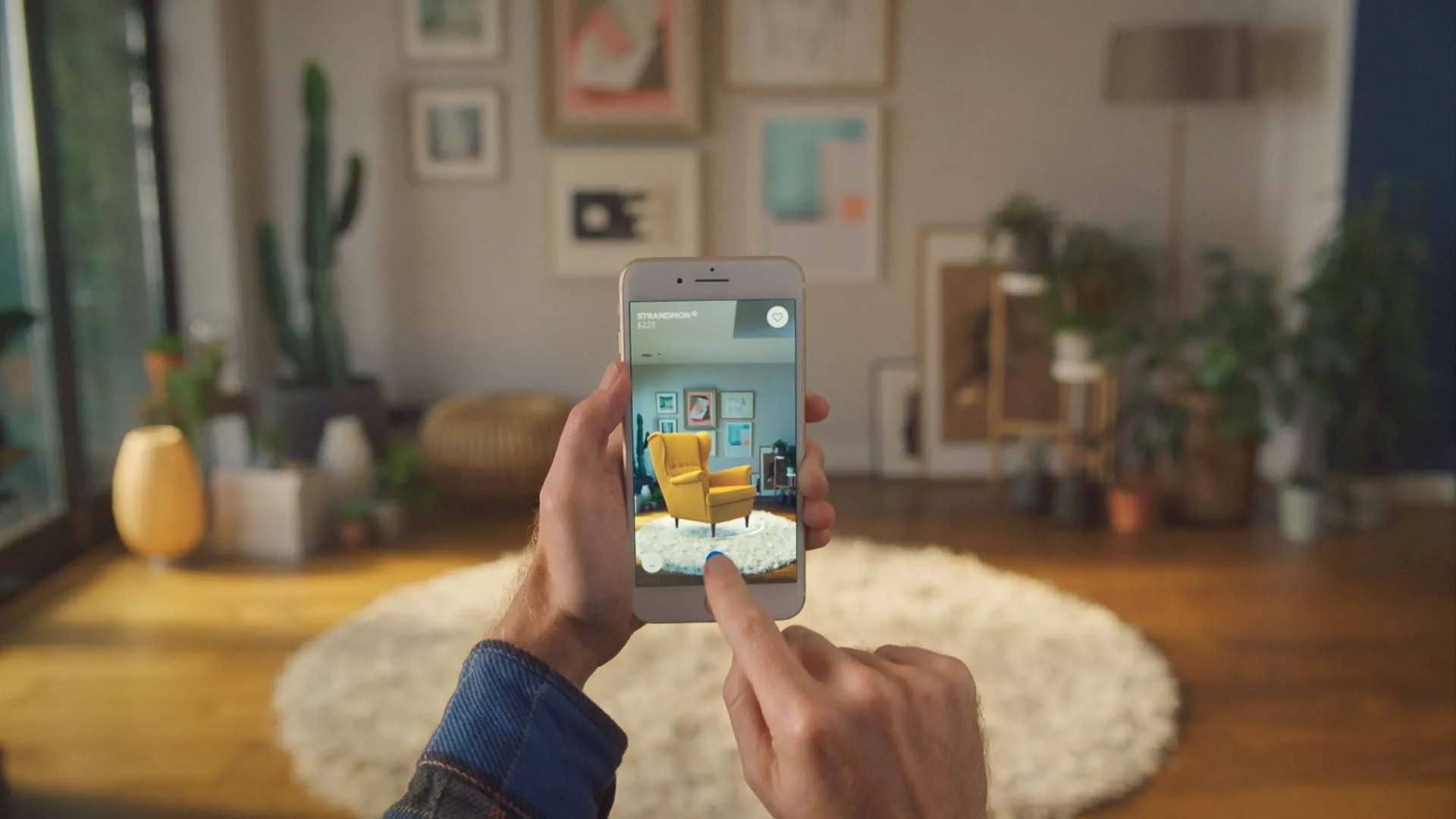

The image shows IKEA’s 3D furniture model
How to develop an e-Commerce mobile app? Step-by-step process
Developing a successful e-commerce mobile app in 2025 requires a structured approach. Here's a comprehensive guide to help you through each phase:
1. Define Your Concept and Target Users
Many e-commerce apps fail because they try to serve everyone and end up serving no one. When you don’t know exactly who your user is, you end up building generic features that don’t truly serve anyone. That’s why the first and most important step is defining your niche and ideal user.
Whether you’re focused on sustainable fashion or curated tech gadgets, knowing your space helps shape the product roadmap. Go deep into user behavior- what they buy, how often they shop, what frustrates them in current apps, and what keeps them loyal. This understanding will guide everything from your UX to your marketing messages.
How to Do It:
- Create user personas detailing demographics, shopping habits, and pain points.
- Use surveys, interviews, or existing data from your website analytics.
- Document these in a simple template or tools like Google Docs or Miro to keep your team aligned.
Example:
If targeting, a fast-fashion app may target Gen Z users seeking quick trend updates, whereas an eco-conscious brand might focus on buyers valuing sustainability and ethical sourcing. To get more clarity, you could use our step-by-step guide to building a dating app..

A flowchart showing the steps to take for defining the concept and target users while developing an e-commerce app.
2. Conduct Competitor and Market Research
It’s easy to get caught up in building features you think users want, until you realize a competitor already offers them, or worse, users didn’t need them in the first place.
Skipping market research often leads to wasted dev hours and missed opportunities.
Studying what similar apps are doing right (or wrong) gives you a head start. It helps you avoid common pitfalls, differentiate your offering, and find untapped angles that competitors may be ignoring. Think of it as creating a shortcut by learning from others’ successes and failures before writing your first line of code.
How to Do It:
- Use tools like SimilarWeb and App Annie to study competitor apps, look at their rankings, reviews, feature sets, and user feedback. ( Also try to identify gaps like poor UX, limited payment options, or slow loading time.)
3. Plan Key Features and User Flow
Many apps fail not because of poor tech, but because users get lost, stuck, or bored before they even reach checkout.
Mapping a clear and intuitive user journey ensures users move smoothly from landing to purchase. At this stage, the goal is not just to list features, but to understand how users will interact with them and in what order.
Planning this early avoids rework later and helps your design and dev teams stay aligned.
How to Do It:
- Outline core features: product browsing, search, wishlist, cart, checkout, payment, order tracking, customer support.
- Use Figma or Adobe XD to create wireframes and interactive prototypes.
- Conduct usability tests with 5-7 representative users to identify pain points before development.
Example:
Airbnb’s app flow uses minimal screens and clear calls to action to reduce steps between discovery and booking
4. Select the Right Tech Stack
Your app's performance, speed, and user experience depend heavily on the technology you use to build it. If you pick the wrong tools, you could end up with an app that’s buggy, slow, or expensive to maintain. The key is to choose tools that fit your goals.
For instance, if you want to launch on both iOS and Android quickly, you don’t need two separate teams. But if you’re building a complex app with animations or AR features, then going for the best-quality option is worth it even if it takes more time.
👉For a detailed breakdown, read our complete guide to iOS app development.
How to Do It:
- For native iOS apps, use Swift, and for Android apps, use Kotlin/Java. These deliver optimal performance but require separate teams.
- For cross-platform, consider Flutter or React Native. These enables faster development and single codebase, but may sacrifice some performance or advanced features.
- Use backend frameworks like Node.js or Django.
Consult with your developers on your budget, timeline, and expected app complexity to pick the right option.

5. Integrate Secure Payment Gateways
If payments fail or feel sketchy, users drop off instantly and rarely come back. Offering limited payment methods or lacking proper encryption can kill trust, especially for first-time users.
The goal here is to make the transaction feel instant, safe, and seamless. Users should never hesitate at the checkout page.
How to Do It:
- Integrate APIs from payment providers like Stripe, PayPal, Razorpay, and Apple Pay.
- Implement SSL encryption and comply with PCI DSS standards.
- Test payments in sandbox modes thoroughly across devices and network conditions.
- Also, consider adding ‘one-click checkout’ options to reduce friction.
Example:
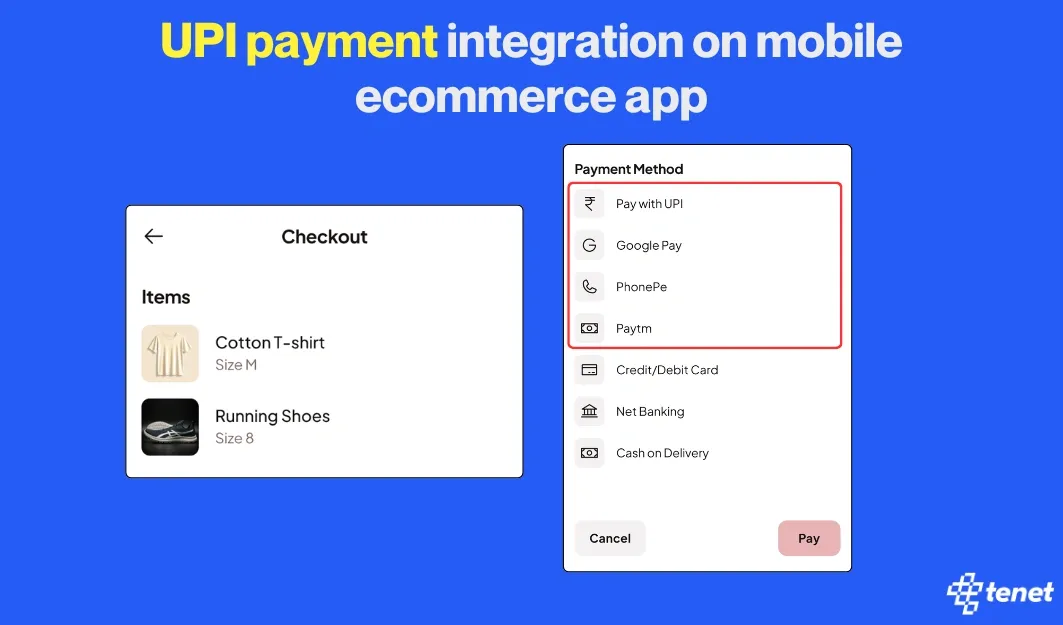
In India, integrating UPI payments via Razorpay can enhance user convenience.
6. Build, Test, and Launch MVP
Launching your app with every feature upfront can be risky and expensive. Instead, start with a Minimum Viable Product (MVP), a version that includes only the essential features your users need to solve their problems.
This approach lets you test your idea in the real world, gather genuine feedback, and fix issues early before investing heavily.
Continuous testing during this phase helps catch bugs and usability problems that no amount of planning can predict.
Using tools to track how users interact with your app provides insights that shape smarter updates, ensuring your app evolves based on real user needs, not assumptions.
How to Do It:
Break development into manageable sprints, focusing on core features. Use:
- TestFlight (iOS) and Google Play Console beta tracks to recruit real users for feedback.
- Monitor crash reports with Firebase Crashlytics and track user behavior with Mixpanel or Amplitude.
- Refine based on real-world usage before full launch.
7. Post-Launch Maintenance and Updates
Launching your app isn’t the finish line, it’s just the beginning. Continuous maintenance and timely updates are important to keep users happy and engaged. By monitoring real user behavior and feedback, you can spot bugs before they become widespread problems and discover which features delight users or cause frustration.
Regularly releasing updates improves app performance, adds new functionality, and shows users that you’re actively invested in their experience. Also, listening closely to reviews and social media conversations helps prioritize what truly matters, increasing retention and long-term success.
How to Do It:
- Use analytics tools like Firebase or Mixpanel to track user behavior.
- Conduct A/B testing to optimize features.
- Schedule regular updates to fix bugs, improve speed, and add features based on feedback.
- Monitor reviews and social media for feedback to prioritize fixes.
Example:
Introduce a loyalty program based on user purchase history to increase retention.
What are the must-have features of a high-converting e-commerce mobile app?
Creating a mobile app that truly converts means blending usability with trust, speed, and personalization. Below are essential features backed by current data and real app examples, all tailored for 2025.
1. User Registration and Profile Management
What it is:
This feature enables users to create and manage personal accounts, making it easier to track orders, save preferences, and personalize their shopping experience.
How to implement:
- Provide multiple registration options: email, mobile number, and social logins (Google, Apple, Facebook).
- Allow guest checkout, but highlight the benefits of account creation (order tracking, faster checkout).
- Let users easily update their profiles, addresses, and payment methods.
- Use mobile-first design: large, tap-friendly buttons and minimal required fields for quick sign-up.
- Ensure data privacy and communicate how user data will be used.
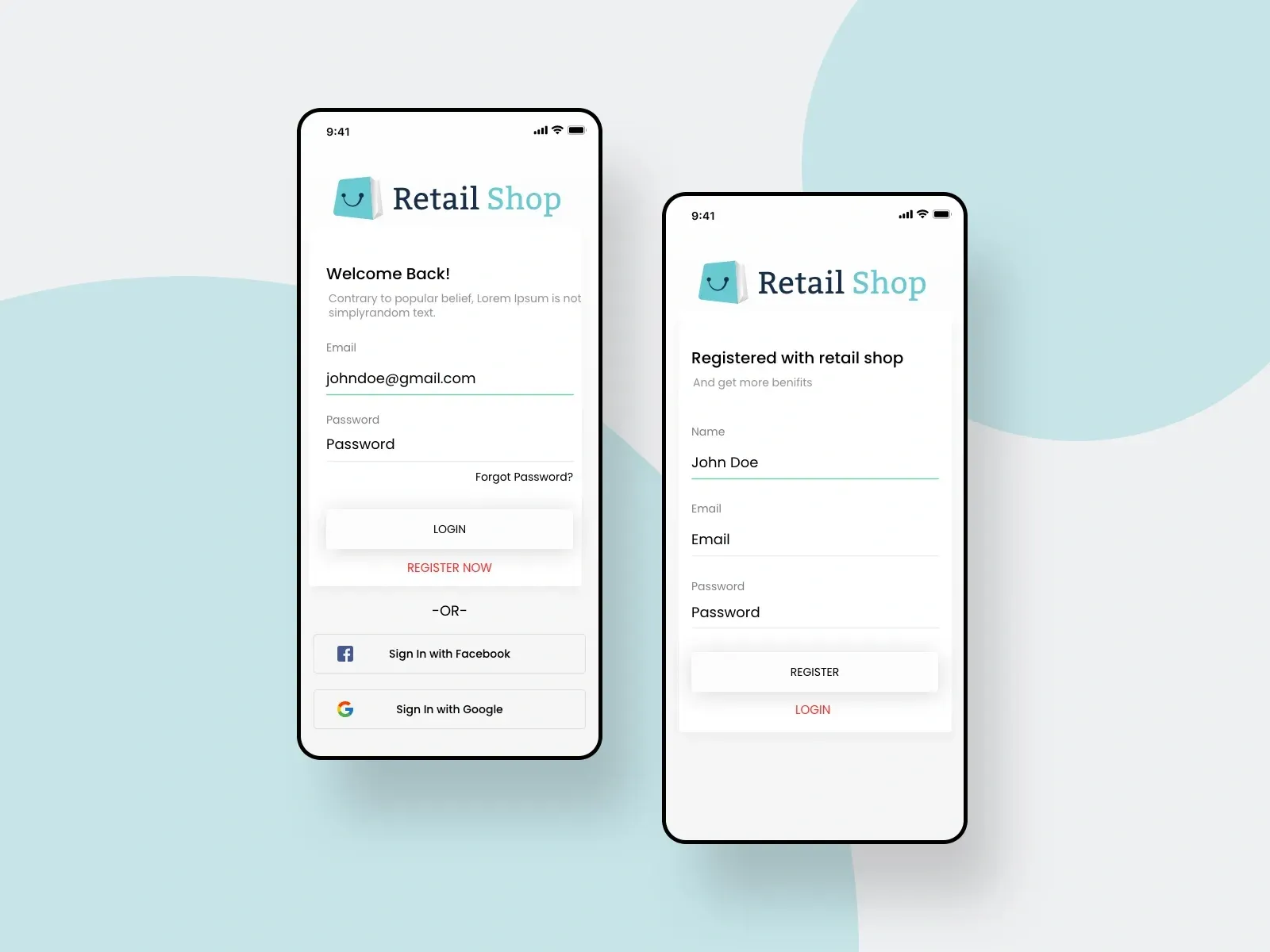
Image showing multiple options to sign in
2. Product Search and Advanced Filtering
What it is:
A powerful search and filtering system helps users quickly find relevant products, reducing friction and boosting conversions.
How to implement:
- Place a prominent search bar at the top of every screen.
- Support auto-suggestions and voice search.
- Offer advanced filters (category, price, brand, rating, availability).
- Use a mobile-first design: filters as collapsible menus or bottom sheets for easy access.
- Display recent searches and trending products.
Example:
Flipkart’s app features a sticky search bar, voice search, and multi-layered filters for price, brand, and ratings.

3. Shopping Cart and Wish List
What it is:
The shopping cart lets users review and edit selected items before checkout, while the wish list saves products for future consideration.
How to implement:
- Keep a persistent cart icon with item count visible at all times.
- Allow users to edit quantities, remove items, or move items to/from the wish list.
- Make the wish list accessible from product pages with a single tap.
- Sync cart and wish list across devices for logged-in users.
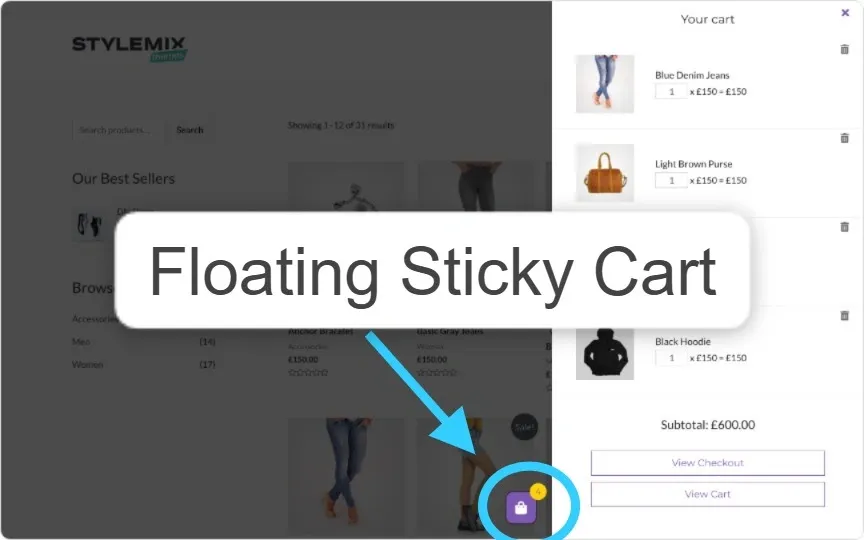
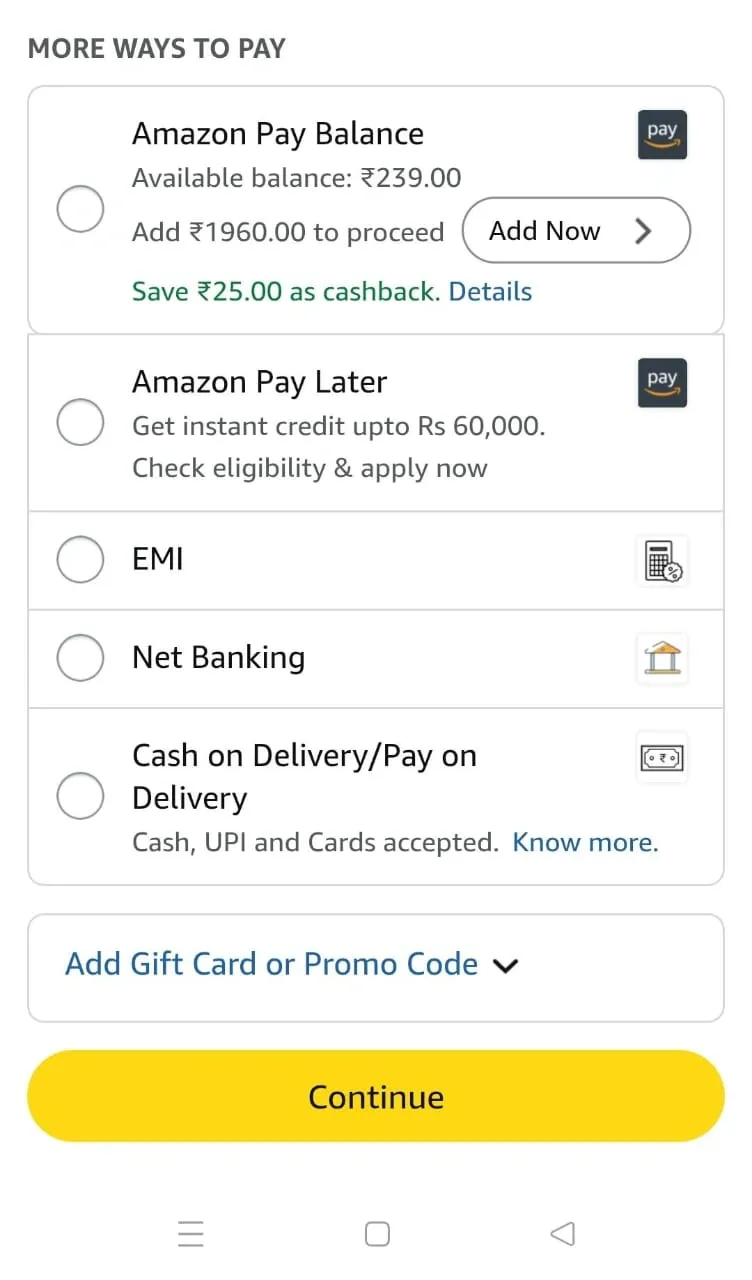
4. Multiple Payment Options
What it is:
Offering various secure payment methods reduces friction and cart abandonment, catering to diverse user preferences.
How to implement:
- Integrate major credit/debit cards, UPI, digital wallets (Paytm, Google Pay), and cash on delivery.
- Enable one-tap payment with saved cards and wallets.
- Clearly show all payment options at checkout, and highlight security measures.
- Support local payment methods for global reach.
Example:
Amazon provides a range of payment options, including wallets, UPI, cards, and cash on delivery, all accessible on one screen.
5. Order Tracking and Management
What it is:
Allows users to monitor their order status in real time and manage returns or cancellations, enhancing trust and reducing support queries.
How to implement:
- Show a detailed order timeline with status updates (confirmed, shipped, out for delivery, delivered).
- Enable push/email notifications for every order stage.
- Allow users to initiate returns or cancellations directly from the order details page.
Example:
Amazon displays a visual order progress bar and allows users to request returns or contact support from the same screen.
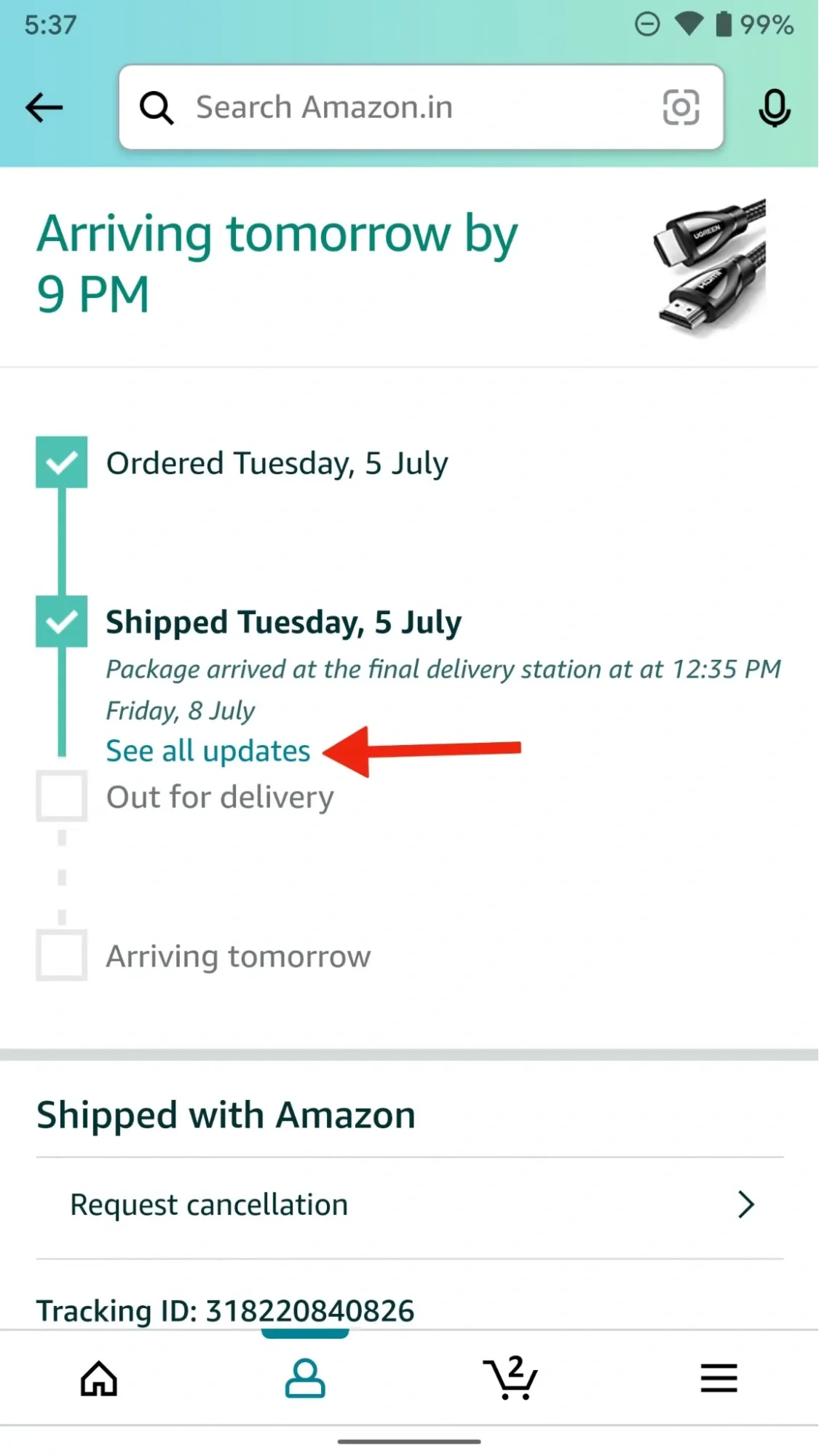
6. Push Notifications
What it is:
Push notifications keep users engaged with timely updates, offers, and reminders, driving repeat visits and conversions.
How to implement:
- Send personalized notifications about promotions, order status, and abandoned carts.
- Allow users to control notification preferences in settings.
- Use segmentation to send relevant messages and avoid spamming.
- Schedule notifications for optimal engagement times.
Example:
Myntra's app sends notifications for flash sales, discounts and order updates, with clear opt-in controls.
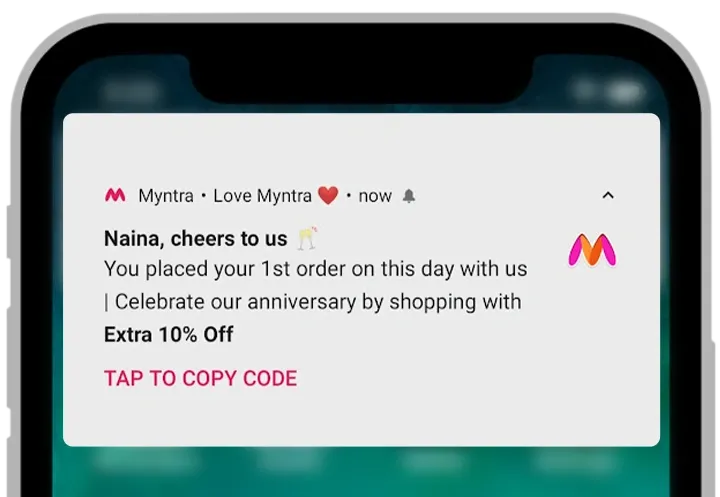
7. Customer Reviews and Ratings
What it is:
Customer reviews and ratings build trust, help users make decisions, and directly increase conversions.
How to implement:
- Display ratings and reviews prominently on product pages.
- Allow users to filter products by rating.
- Encourage verified buyers to leave feedback with post-purchase prompts.
- Highlight top reviews and display review images when possible.
Example:
Amazon’s app features a detailed review section with filters for verified purchases, star ratings, and user-uploaded images.
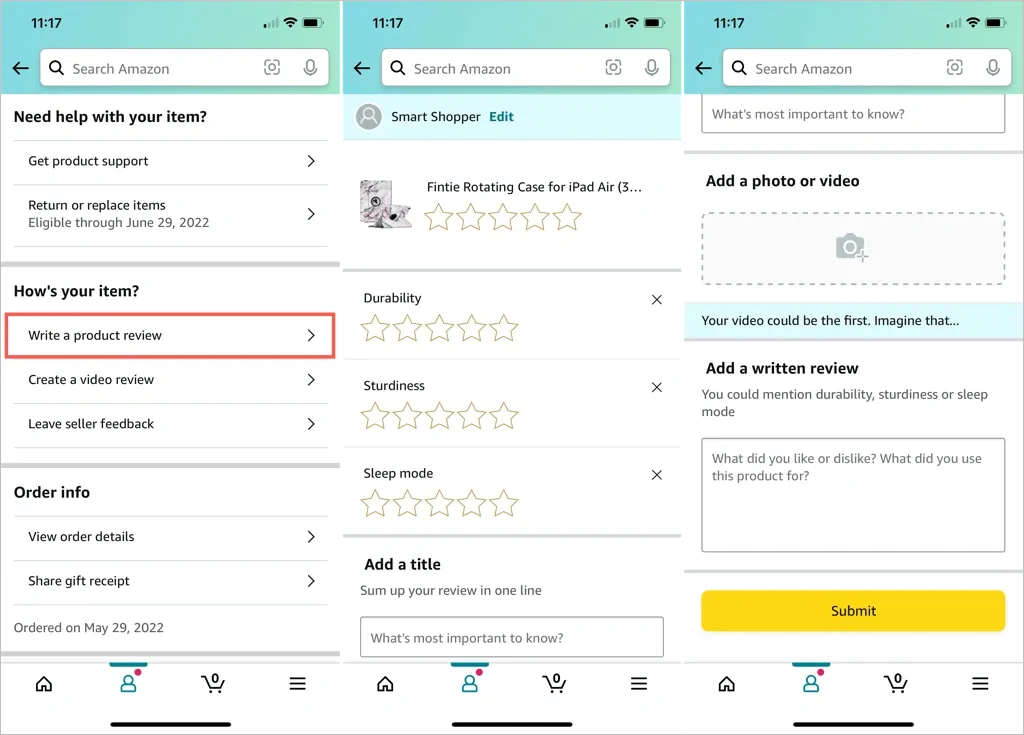
8. Chat Support and Chatbots
What it is:
Live chat and AI chatbots provide instant help, reducing drop-offs and improving user satisfaction.
How to implement:
- Integrate a chatbot for FAQs and order status, with escalation to live agents as needed.
- Make chat support accessible from every screen.
- Offer quick replies for common queries and allow users to rate support quality.
Example:
Sephora uses an AI chatbot for order support, with seamless handover to human agents if required.

9. Loyalty Programs and Reward Points
What it is:
Loyalty programs encourage repeat purchases by rewarding users with points, discounts, or exclusive perks.
How to implement:
- Award points for purchases, referrals, and reviews.
- Let users redeem points for discounts or gifts.
- Show loyalty status and rewards progress in the user profile.
- Send push notifications about point expiry and special loyalty offers.
Example:
BigBasket’s “bbstar” program offers members exclusive discounts and tracks points in the app.

10. Easy Return and Refund System
What it is:
A simple and transparent return/refund process increases user confidence and reduces purchase hesitation.
How to implement:
- Let users initiate returns directly from the order details page.
- Clearly state return policies and timelines on product and order pages.
- Provide real-time updates on return/refund status via notifications.
- Offer instant refunds to a wallet or the original payment method when possible.
Example:
Flipkart’s app features a clear “Return” button in order details and tracks refund progress step by step.

👉 Further ecommerce-related resources:
- Ecommerce CRO audit: A complete guide with a checklist
- What to include in your ecommerce product page? (New Study)
How long does it take to develop an e-commerce app?
Developing an e-commerce mobile app typically takes 3 to 9 months, depending on the app's complexity, features, and development approach. A basic app with essential features can be built in 3–6 months, while a complex, feature-rich app may require 9 months or more.
This timeline depends on several variables such as:
- App’s overall complexity (simple, moderate, or advanced features)
- Number of screens or user flows
- Level of design customization (template-based vs. custom UI/UX)
- Integration needs like payment gateways, CRMs, or third-party APIs
- Platform choice: native (iOS/Android separately) or cross-platform (e.g., Flutter, React Native)
- Size and experience of the development team
- Number of feedback and testing cycles during development
Each of these factors can either accelerate or slow down your go-to-market plan.
To help you plan better, we’ve outlined the typical stages involved in developing an e-commerce app, along with their estimated durations.
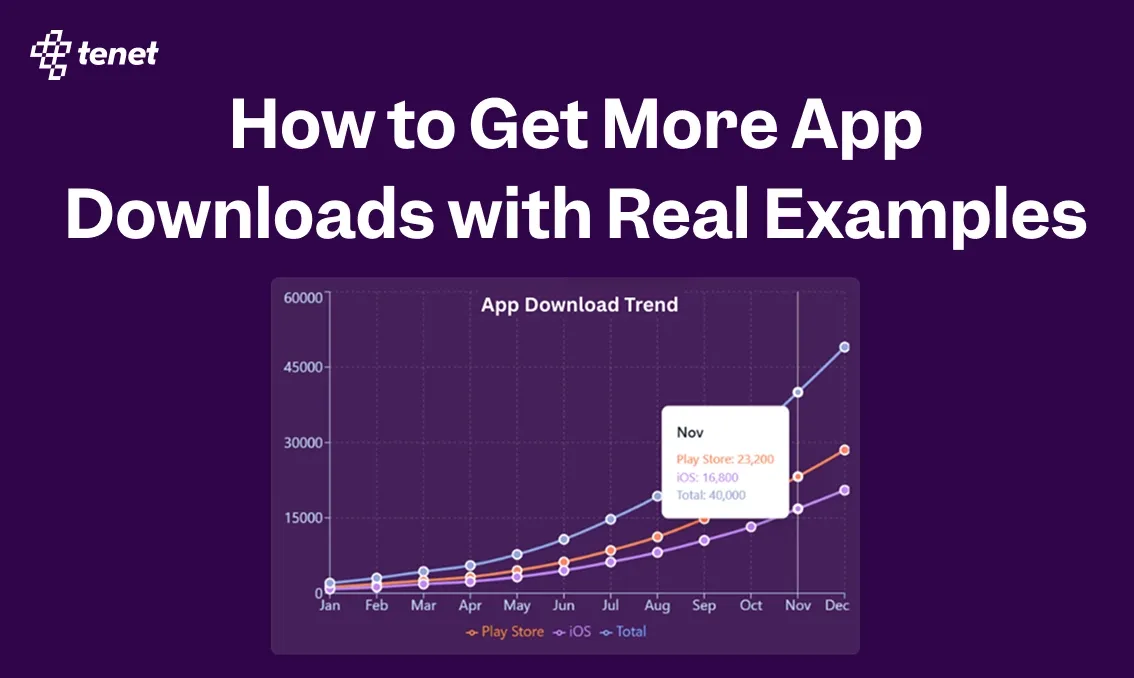
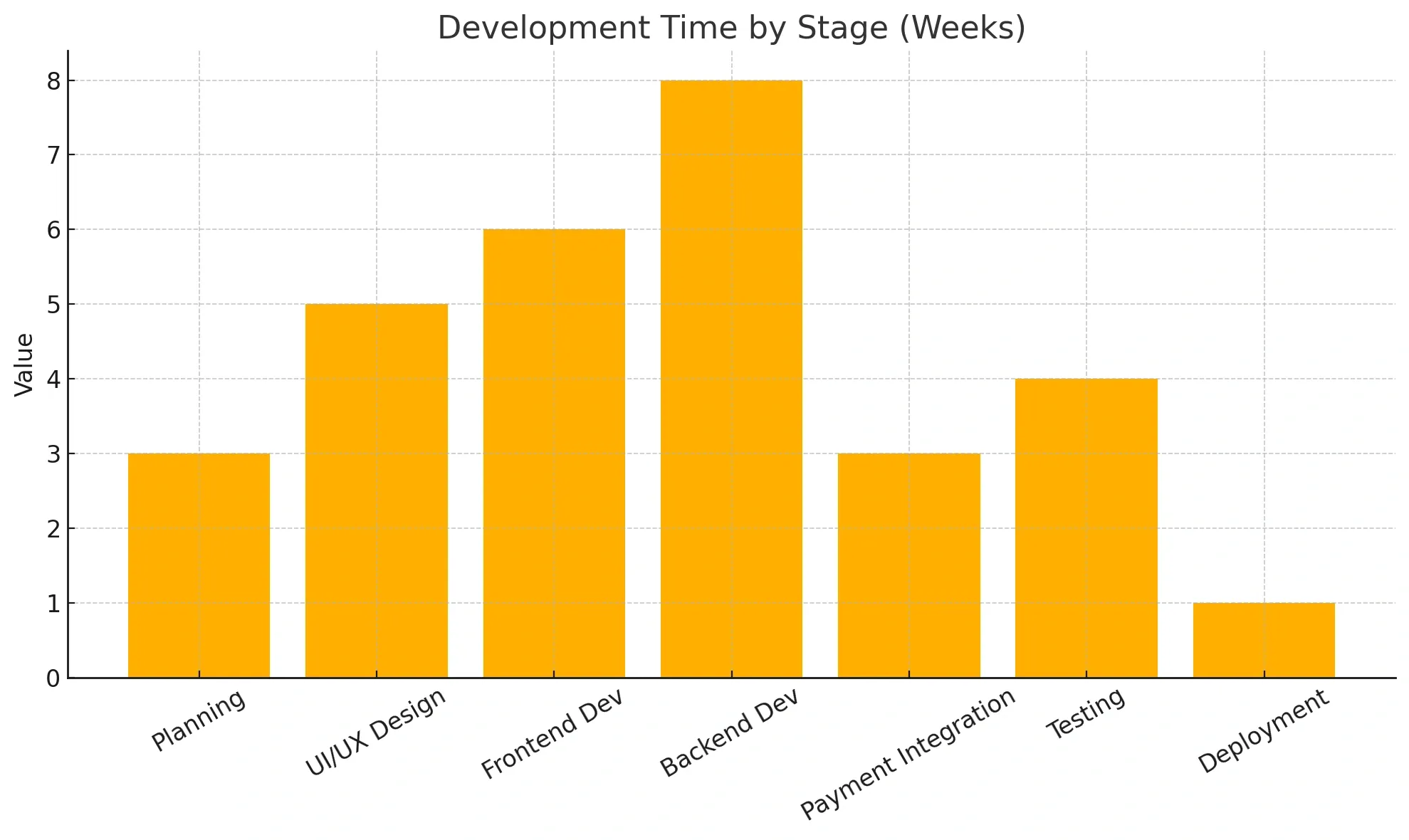
Ecommerce mobile app development timeline breakdown by feature
Here’s a chart to understand ecommerce app development time by stage (Weeks):
Why Choose Tenet for E-commerce Mobile App Development?
The global eCommerce market is projected to reach $5 trillion by 2025, making it crucial to partner with experts who can turn clicks into conversions.
Our agency stands out with a proven approach that combines data-driven strategies and conversion-focused design to maximize your ROI and grow your online sales.
Here’s what sets Tenet apart as a mobile app development agency:
Our clients trust us, reflected in a 98% satisfaction rate and strong repeat business. Tenet also holds top industry ratings, including 4.7 stars on Google and 5 stars on Clutch and GoodFirms.
Trusted by global brands like Lazada, Sephora, and DoorDash, we specialize in reducing cart abandonment through improved UX and conversion rate optimization. Plus, we optimize ad spend and continuously refine your eCommerce experience for lasting growth.

Let’s explore what we can create together:
FAQs
How do I choose the right tech stack for my e-commerce app?
Choosing the right tech stack depends on your app’s goals, budget, and target audience. Consider factors like
- Scalability and speed
- Security features
- Native (Swift, Kotlin) vs. cross-platform (React Native, Flutter)
- Select backend technologies like Node.js or Ruby on Rails that support your app’s features.
Consulting experienced developers ensures you pick a stack that supports growth and smooth performance.
What payment gateways should I integrate into my e-commerce app?
Integrate popular, secure payment gateways to accommodate your customers. Common options include PayPal and Stripe for global reach, Apple Pay and Google Pay for mobile users, or local payment options suited to your market
Make sure these gateways support secure transactions and comply with industry standards like PCI-DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) to protect customer data and increase trust.
How can I make my e-commerce app stand out from competitors?
To stand out, focus on delivering a fast and smooth user experience. Incorporate personalized recommendations and unique features such as augmented reality or loyalty rewards. Excellent customer support and regular updates also help build user loyalty. These factors keep your app engaging and competitive in a crowded market.
What are the common mistakes to avoid in e-commerce app development?
These are the common mistakes to avoid in e-commerce app development, like complex navigation or confusing UI, slow load times, limited payment options, poor mobile optimization and weak security can frustrate users.
Also, don’t ignore user feedback or skip thorough testing. These mistakes reduce customer satisfaction and can harm your app’s success and sales.
How do e-commerce apps ensure customer data security?
E-commerce apps protect data by encrypting it with SSL/TLS protocols, using biometric and two-factor authentication, and complying with privacy laws like GDPR. Regular security audits and trusted payment gateways add extra layers of safety. These measures help build customer trust and prevent data breaches.
What is the best way to handle returns and refunds in an e-commerce app?
Make returns simple by providing a clear, accessible policy and automating status updates throughout the process. Offer quick refunds and responsive customer support to resolve issues efficiently. A smooth returns experience increases customer trust and encourages repeat business.
How can I increase user retention for my e-commerce mobile app?
Increase retention by sending personalized push notifications, implementing loyalty and rewards programs, and making reordering easy with fast checkout options. Regular updates and improvements ensure the app stays relevant and enjoyable, keeping users engaged and coming back.
Should I build a native app or a cross-platform ecommerce app?
Native apps provide better performance and deeper device integration, but can be more costly and time-consuming. Cross-platform apps save development time and budget by working across devices, though sometimes with performance trade-offs. Choose based on your budget, timeline, and app complexity to balance quality and cost-effectiveness.
How important is app UI/UX design in e-commerce success?
UI/UX design is crucial because it shapes the entire shopping experience. A clean, intuitive design reduces frustration, lowers cart abandonment, and builds trust. Good UI/UX encourages customers to explore, engage, and buy more, directly impacting sales and long-term loyalty.
Get your free ecommerce app development proposal now
Get your free ecommerce app development proposal now

Got an idea on your mind?
We’d love to hear about your brand, your visions, current challenges, even if you’re not sure what your next step is.
Let’s talk